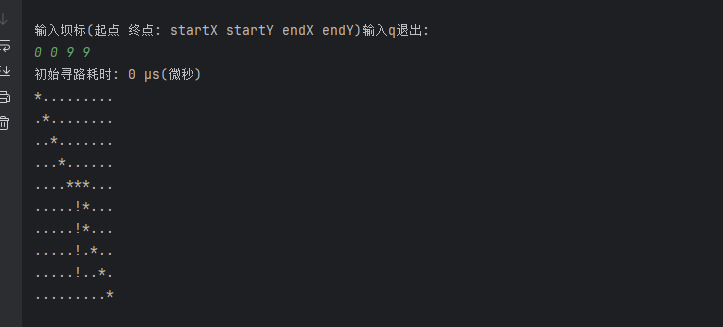
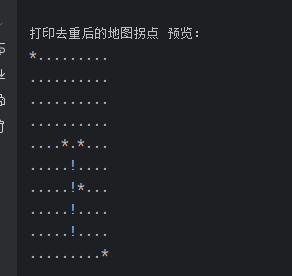
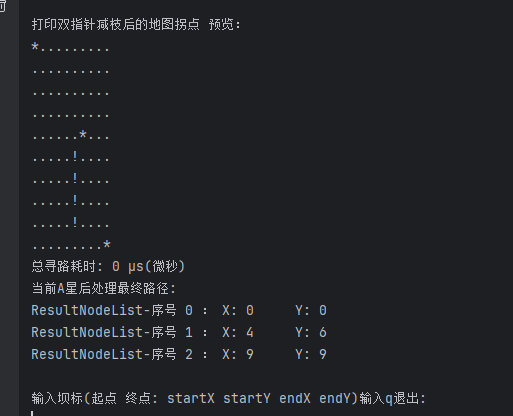
学习自动寻路过程中,对于A*算法的学习,在此记录一下。
寻路算法的核心其实是构建网格系统 。网格系统将连续的游戏世界离散化成一个个格子,这样算法才能在可计算的时间内找到路径。
还有一种是路标形式,减少了大量无用的节点:
这里只做了解。
网格系统
首先是基础单元格,分为了可通行、障碍物、高代价通行、低代价通行;高代价通行、低代价通行可以用来模拟杂草和道路
/** 单元格类型 */
export enum CellType {
WALKABLE, // 可通行
OBSTACLE, // 障碍物
ROAD_HighCost, // 道路(高代价)
ROAD_LowCost // 道路(低代价)
}
/** 网格单元 */
export class GridCell {
public x: number;
public y: number;
public type: CellType;
public cost: number; // 移动代价
constructor(x: number, y: number, type: CellType = CellType.WALKABLE) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.type = type;
this.cost = this.getCostByType(type);
}
private getCostByType(type: CellType): number {
switch (type) {
case CellType.WALKABLE: return 1; // 可通行
case CellType.OBSTACLE: return Infinity; // 不可通行
case CellType.ROAD_HighCost: return 2; // 高代价
case CellType.ROAD_LowCost: return 0.5; // 低代价
default: console.warn("Invalid cell type: " + type); return Infinity; // 类型错误
}
}
public isWalkable(): boolean {
return this.cost < Infinity;
}
}
然后是网格系统,用于初始化&管理网格
/** 网格系统 */
export class GridSystem {
private width: number; // 网格宽度(格子数)
private height: number; // 网格高度(格子数)
private cellSize: number; // 每个格子的大小(单位)
private cells: GridCell[][]; // 二维数组存储所有格子
constructor(width: number, height: number, cellSize: number) {
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
this.cellSize = cellSize;
this.cells = [];
this.initializeGrid();
}
/** 初始化网格 */
private initializeGrid() {
for (let x = 0; x < this.width; x++) {
this.cells[x] = [];
for (let y = 0; y < this.height; y++) {
this.cells[x][y] = new GridCell(x, y, CellType.WALKABLE);
}
}
}
/** 坐标转网格坐标 */
posToGrid(pos: Vec3): { x: number, y: number } {
return {
x: Math.floor(pos.x / this.cellSize),
y: Math.floor(pos.y / this.cellSize)
};
}
/** 网格坐标转坐标(格子中心点) */
gridToPos(gridX: number, gridY: number): Vec3 {
return new Vec3(
gridX * this.cellSize + this.cellSize / 2,
gridY * this.cellSize + this.cellSize / 2
);
}
/** 获取指定坐标格子 */
getCell(gridX: number, gridY: number): GridCell | null {
if (this.isValidGridPosition(gridX, gridY)) {
return this.cells[gridX][gridY];
}
return null;
}
/** 检查网格坐标是否有效 */
isValidGridPosition(gridX: number, gridY: number): boolean {
return gridX >= 0 && gridX < this.width &&
gridY >= 0 && gridY < this.height;
}
/** 设置格子类型 */
setCellType(gridX: number, gridY: number, type: CellType): boolean {
if (this.isValidGridPosition(gridX, gridY)) {
this.cells[gridX][gridY] = new GridCell(gridX, gridY, type);
return true;
}
return false;
}
/** 通过坐标设置障碍物 */
setObstacleByPos(pos: Vec3): boolean {
const gridPos = this.posToGrid(pos);
return this.setCellType(gridPos.x, gridPos.y, CellType.OBSTACLE);
}
/** 检查位置是否可通行 */
isWalkable(gridX: number, gridY: number): boolean {
const cell = this.getCell(gridX, gridY);
return cell ? cell.isWalkable() : false;
}
/** 获取移动代价 */
getMoveCost(gridX: number, gridY: number): number {
const cell = this.getCell(gridX, gridY);
return cell ? cell.cost : Infinity;
}
/** 获取临近格子(8方向或4方向) */
getNeighbors(gridX: number, gridY: number, allowDiagonal: boolean = true): GridCell[] {
const neighbors: GridCell[] = [];
// 4方向:上、右、下、左
const directions4 = [
{ dx: 0, dy: 1 }, // 上
{ dx: 1, dy: 0 }, // 右
{ dx: 0, dy: -1 }, // 下
{ dx: -1, dy: 0 } // 左
];
// 8方向:上、右上、右、右下、下、左下、左、左上
const directions8 = [
{ dx: 0, dy: 1 }, // 上
{ dx: 1, dy: 1 }, // 右上
{ dx: 1, dy: 0 }, // 右
{ dx: 1, dy: -1 }, // 右下
{ dx: 0, dy: -1 }, // 下
{ dx: -1, dy: -1 }, // 左下
{ dx: -1, dy: 0 }, // 左
{ dx: -1, dy: 1 } // 左上
];
const directions = allowDiagonal ? directions8 : directions4;
for (const dir of directions) {
const newX = gridX + dir.dx;
const newY = gridY + dir.dy;
if (this.isValidGridPosition(newX, newY) && this.isWalkable(newX, newY)) {
const cell = this.getCell(newX, newY);
if (cell) {
neighbors.push(cell);
}
}
}
return neighbors;
}
/** 获取网格信息 */
getGridInfo() {
return {
width: this.width,
height: this.height,
cellSize: this.cellSize,
totalCells: this.width * this.height
};
}
}
A*算法
A*算法原理计算周围每个格子的 实际代价 + 估计代价 选择最小的进行扩展。
- 实际代价,从起点到此处的实际代价
- 估计代价,从此处到终点的估计代价(启发函数),有多种算法(
calculateHeuristic)。
在扩展时对于来向进行记录,当扩展到终点时停止,反向追踪路径,由此得到;这里用的 parent 属性来记录来向。
计算时每个格子作为一个单个节点:
import { Color, Graphics, Vec3 } from "cc";
import { GridSystem } from "./GridSystem";
export class AStarNode {
public x: number;
public y: number;
public gCost: number = 0; // 从起点到当前节点的实际代价
public hCost: number = 0; // 从当前节点到终点的启发式估计代价
public parent: AStarNode | null = null;
constructor(x: number, y: number) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
/** 总代价 f = g + h */
get fCost(): number {
return this.gCost + this.hCost;
}
/** 比较两个节点是否相同 */
equals(other: AStarNode): boolean {
return this.x === other.x && this.y === other.y;
}
/** 转换为字符串键,用于Set/Map */
get key(): string {
return `${this.x},${this.y}`;
}
/** 生成key */
static generateKey(x: number, y: number): string {
return `${x},${y}`;
}
}
A*算法核心:
export class AStarPathfinding {
private grid: GridSystem;
constructor(grid: GridSystem) {
this.grid = grid;
}
/**
* 寻路
* @param startPos 起点坐标
* @param endPos 终点坐标
*/
findPath(startWorld: Vec3, endWorld: Vec3): Vec3[] {
// 转换坐标
const startGrid = this.grid.posToGrid(startWorld);
const endGrid = this.grid.posToGrid(endWorld);
console.log(`开始寻路: (${startGrid.x},${startGrid.y}) -> (${endGrid.x},${endGrid.y})`);
// 检查起点和终点是否有效
if (!this.grid.isValidGridPosition(startGrid.x, startGrid.y) ||
!this.grid.isValidGridPosition(endGrid.x, endGrid.y)) {
console.warn("起点或终点不在网格范围内");
return [];
}
if (!this.grid.isWalkable(startGrid.x, startGrid.y)) {
console.warn("起点不可通行");
return [];
}
if (!this.grid.isWalkable(endGrid.x, endGrid.y)) {
console.warn("终点不可通行");
return [];
}
// 如果起点就是终点
if (startGrid.x === endGrid.x && startGrid.y === endGrid.y) {
return [this.grid.gridToPos(endGrid.x, endGrid.y)];
}
// 执行A*算法
const pathNodes = this.findPathAStar(startGrid, endGrid);
if (pathNodes.length === 0) {
console.warn("未找到路径");
return [];
}
// 转换为坐标路径
const worldPath = pathNodes.map(node =>
this.grid.gridToPos(node.x, node.y)
);
console.log(`找到路径,包含 ${worldPath.length} 个点`);
return worldPath;
}
/** A*算法核心实现 */
private findPathAStar(start: {x: number, y: number}, end: {x: number, y: number}): AStarNode[] {
// 开放列表(待检查的节点)
const openSet: AStarNode[] = [];
// 关闭列表(已检查的节点)
const closedSet: Set<string> = new Set();
// 记录节点
const nodeMap: Map<string, AStarNode> = new Map();
// 创建起始节点
const startNode = new AStarNode(start.x, start.y);
startNode.gCost = 0;
startNode.hCost = this.calculateHeuristic(start.x, start.y, end.x, end.y);
openSet.push(startNode);
while (openSet.length > 0) {
// 找到fCost最小的节点(开放列表中)
let currentNode = this.getLowestFCostNode(openSet);
// 如果找到终点,重构路径
if (currentNode.x === end.x && currentNode.y === end.y) {
return this.retracePath(startNode, currentNode);
}
// 从开放列表移到关闭列表
this.removeFromArray(openSet, currentNode);
closedSet.add(currentNode.key);
// 检查所有邻居节点
const neighbors = this.grid.getNeighbors(currentNode.x, currentNode.y, true);
for (const neighborCell of neighbors) {
// 查找是否已经创建节点
let neighborNode = nodeMap.get(AStarNode.generateKey(neighborCell.x, neighborCell.y));
if (!neighborNode) {
// 新建并记录
neighborNode = new AStarNode(neighborCell.x, neighborCell.y);
nodeMap.set(neighborNode.key, neighborNode);
}
// 跳过已在关闭列表的节点
if (closedSet.has(neighborNode.key)) {
continue;
}
// 计算新的gCost
const newGCost = currentNode.gCost + this.getDistanceBetween(currentNode, neighborNode) * neighborCell.cost;
// 如果到达节点的新路径开销更低,或者邻居节点不在开放列表中
if (newGCost < neighborNode.gCost || !this.isInArray(openSet, neighborNode)) {
// 更新邻居节点
neighborNode.gCost = newGCost;
neighborNode.hCost = this.calculateHeuristic(neighborNode.x, neighborNode.y, end.x, end.y);
// 父节点用于反向回溯
neighborNode.parent = currentNode;
// 如果不在开放列表,添加进去
if (!this.isInArray(openSet, neighborNode)) {
openSet.push(neighborNode);
}
}
}
}
// 开放列表为空,未找到路径
return [];
}
/** 计算启发式函数(估计代价) */
private calculateHeuristic(x1: number, y1: number, x2: number, y2: number): number {
// 方法1:曼哈顿距离(适合4方向移动)
// return Math.abs(x1 - x2) + Math.abs(y1 - y2);
// 方法2:欧几里得距离(适合任意方向移动)
// const dx = Math.abs(x1 - x2);
// const dy = Math.abs(y1 - y2);
// return Math.sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy);
// 方法3:切比雪夫距离(适合8方向移动)
return Math.max(Math.abs(x1 - x2), Math.abs(y1 - y2));
// 方法4:对角线距离(推荐用于8方向)
// const dx = Math.abs(x1 - x2);
// const dy = Math.abs(y1 - y2);
// return Math.max(dx, dy) + (Math.sqrt(2) - 1) * Math.min(dx, dy);
}
/** 计算两个节点间的实际距离 */
private getDistanceBetween(nodeA: AStarNode, nodeB: AStarNode): number {
const dx = Math.abs(nodeA.x - nodeB.x);
const dy = Math.abs(nodeA.y - nodeB.y);
if (dx > dy) {
return 1.4 * dy + 1.0 * (dx - dy); // 对角线+直线
} else {
return 1.4 * dx + 1.0 * (dy - dx);
}
}
/** 从开放列表中找到fCost最小的节点 */
private getLowestFCostNode(nodes: AStarNode[]): AStarNode {
let lowestNode = nodes[0];
for (let i = 1; i < nodes.length; i++) {
if (nodes[i].fCost < lowestNode.fCost ||
(nodes[i].fCost === lowestNode.fCost && nodes[i].hCost < lowestNode.hCost)) {
lowestNode = nodes[i];
}
}
return lowestNode;
}
/** 重构路径(从终点反向追踪到起点) */
private retracePath(startNode: AStarNode, endNode: AStarNode): AStarNode[] {
const path: AStarNode[] = [];
let currentNode: AStarNode | null = endNode;
while (currentNode !== null && !currentNode.equals(startNode)) {
path.push(currentNode);
currentNode = currentNode.parent;
}
path.reverse();
return path;
}
/** 工具函数:从数组中移除节点 */
private removeFromArray(array: AStarNode[], node: AStarNode): void {
const index = array.findIndex(n => n.equals(node));
if (index !== -1) {
array.splice(index, 1);
}
}
/** 工具函数:检查节点是否在数组中 */
private isInArray(array: AStarNode[], node: AStarNode): boolean {
return array.some(n => n.equals(node));
}
}
实例
构建了一个 8*8 的网格空间,让角色在上面移动。
怎么根据返回的位置数组进行移动
这里使用在 update 中更新位置来实现:
/** 角色节点 */
@property(Node) character: Node;
/** 用来标记当前移动状态 */
private isMoving: boolean = false;
/** 用来接收返回的位置数组 */
private currentPath: Vec3[] = [];
update(deltaTime: number) {
if (!this.isMoving || this.currentPath.length === 0) return;
this.followPath(deltaTime);
}
private followPath(deltaTime: number) {
const currentTarget = this.currentPath[0];
const currentWorldPos = this.character.getComponent(UITransform).convertToWorldSpaceAR(Vec3.ZERO);
const currentPos = this.node.getComponent(UITransform).convertToNodeSpaceAR(currentWorldPos);
const direction = new Vec3();
Vec3.subtract(direction, currentTarget, currentPos);
const distance = direction.length();
if (distance < 2) {
// 到达当前路径点
this.currentPath.shift();
if (this.currentPath.length === 0) {
// 到达终点
this.isMoving = false;
console.log("到达目标!");
return;
}
} else {
// 移动向当前路径点
direction.normalize();
const moveDistance = this.moveSpeed * deltaTime;
const newPos = moveDistance >= distance ?
currentTarget.clone() :
currentPos.clone().add(direction.multiplyScalar(moveDistance));
const worldPos = this.node.getComponent(UITransform).convertToWorldSpaceAR(newPos);
this.character.setPosition(this.character.parent.getComponent(UITransform).convertToNodeSpaceAR(worldPos));
// 更新朝向
this.updateRotation(direction);
}
}
private updateRotation(direction: Vec3) {
const angle = Math.atan2(direction.y, direction.x) * 180 / Math.PI;
this.character.setRotationFromEuler(0, 0, angle);
}
效果
绿色:低代价
黄色:高代价
红色:障碍
青色:表示 开放列表(待检查的节点)openSet
暗青色:表示 关闭列表(已检查的节点)closedSet
鲜绿色:表示 retracePath 重构路径(从终点反向追踪到起点)
4向:
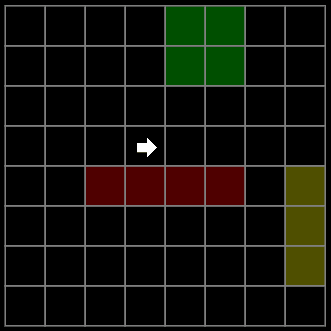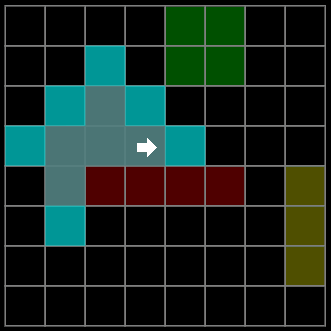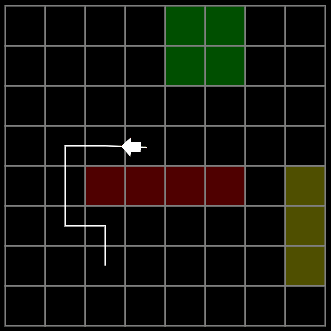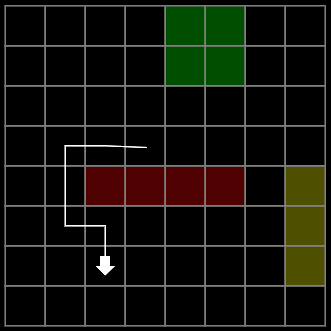
8向: