通常来说,小游戏的用户数据都会保存在本地,一旦用户把包删掉了,里面的游戏数据也会跟着没掉,一切都要从头再来。而想要把用户的数据保存下来就得用到服务器,把数据存在服务器里面,这样就不怕用户数据丢失了。
下面我用本地简单模拟下游戏客户端和服务端的交互流程。
用node.js简单搭建个本地服务器,然后连接一下数据库。
const mysql = require('mysql');
const express = require("express");
const bodyParser = require('body-parser');
const server = express();//服务器地址http://127.0.0.1:3003/
server.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({ extended: false }))
//设置跨域访问
server.all("*", function (request, response, next) {
//设置允许跨域的域名,*代表允许任意域名跨域
response.header("Access-Control-Allow-Origin", "*");
//允许的header类型
response.header("Access-Control-Allow-Headers", "content-type");
//跨域允许的请求方式
response.header("Access-Control-Allow-Methods", "DELETE,PUT,POST,GET,OPTIONS");
switch (request.url) {
case '/login':
break;
default:
break;
}
})
/**绑定端口 */
server.listen(3003, () => {
});
/**数据库处理 */
const connection = mysql.createConnection({
host: 'localhost',
database: 'test',
user: 'root',
password: '123'
});
connection.connect();
/**对数据库进行操作*/
function connectionQuery(sql, value, callback) {
connection.query(sql, value, (error, results, fields) => {
if (error) {
callback(error, null);
return;
}
callback(null, results);
});
}
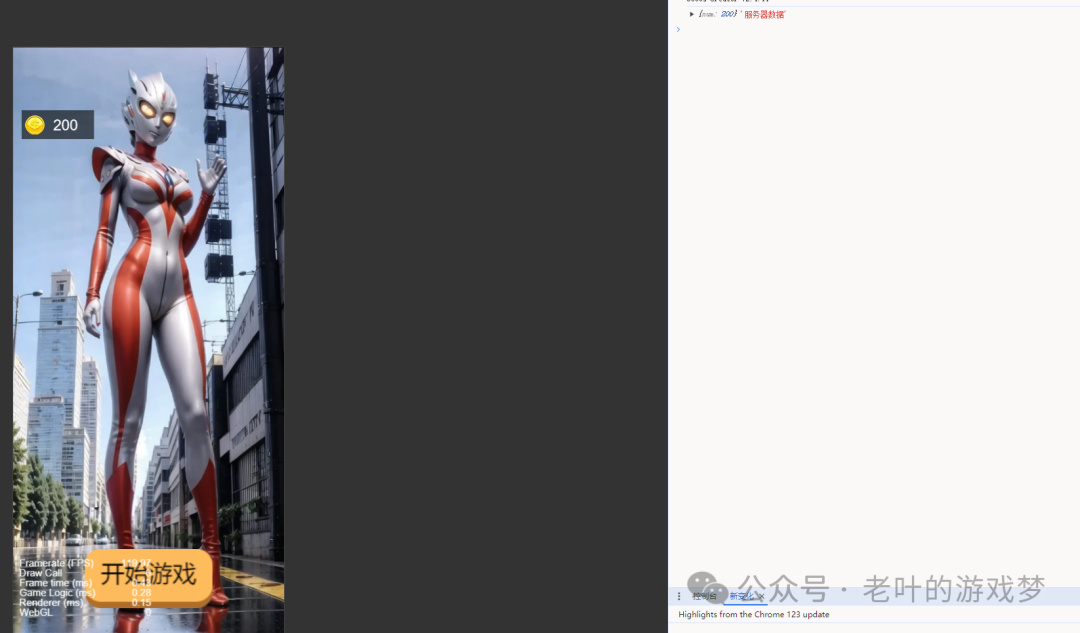
然后我们进入游戏之前,请求一下服务器,把服务器的数据赋值到本地。服务器添加登录接口的请求处理,下发服务端数据,我们用个最简单的金币数据为例子。
case '/login':
connectionQuery('select * from coin', null, (error, res) => {
if (error) {
throw error;
}
response.send(JSON.stringify(res[0]));
})
break;
客户端就会接受到服务端下发下来的金币数据,对界面进行刷新。
StartScreen.singleton.sendRequerst('GET', 'login', {}, null, (err,res) => {
if(err) {
//本地数值直接赋值或者让其禁止进入游戏
}
console.log(res, '服务器数据');
//进行界面刷新
StartScreen.singleton.serverData = res;
this.coinNode.getChildByName('text').getComponent(cc.Label).string = StartScreen.singleton.serverData.num;
cc.assetManager.loadBundle('panel',(error,res) => {
if(error) {return cc.log('资源加载失败',error,res)};
res.load('HomePanel',cc.Prefab, (error,prefab:cc.Prefab) => {
if(error) {return cc.log('资源加载失败',error,res)};
const node = cc.instantiate(prefab);
node.parent = this.node;
})
})
});
更改数据也是同理,更改数据的时候,把要跟新的数据上传到服务端,服务端那边根据客户端的数据对数据库的数据进行更新处理,再返回给客户端,客户端进行ui界面的刷新。
case '/update':
let data = '';
request.on("data", function (chunk) {
data += chunk;
});
request.on("end", function () {
if (data != '') {
connectionQuery(`update coin set num=?`, [JSON.parse(data).num], (error, res) => {
if (error) {
throw error;
}
connectionQuery('select * from coin', null, (error, res) => {
if (error) {
throw error;
}
response.send(200, JSON.stringify(res[0]));
})
})
} else {
response.send(200);
}
});
break;
通过post上传数据到服务端,这样我们就能实现数据的同步 。
StartScreen.singleton.sendRequerst('POST', 'update', {num: 3600}, null, (err,res) => {
if(err) {
//本地数值直接赋值或者让其禁止进入游戏
}
console.log(res, '更新后服务器数据');
//进行界面刷新
StartScreen.singleton.serverData = res;
this.coinNode.getChildByName('text').getComponent(cc.Label).string = StartScreen.singleton.serverData.num;
});
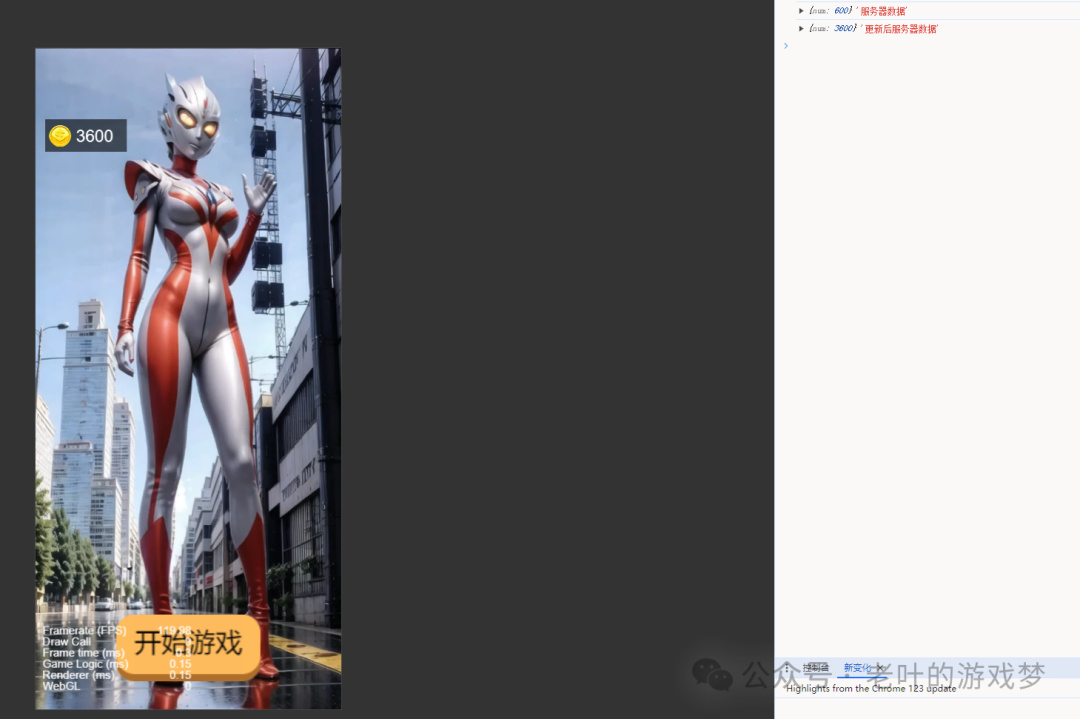
通过服务端对数据的存放,可以做到数据的校验及保存,这样用户把本地的包删掉了,但是用户身上的数据仍然存在服务器上面,下次用户进来,他的数据仍然没变。
数据存在服务端可以对用户的交互行为进行校验,避免用户开挂刷数据。分析用户行为,为游戏的下一次更新和改进做准备。
