点击上方码不了一点+关注和★ 星标
引言
在《只狼》《塞尔达传说》等大作中,你是否见过绳桥摇曳的逼真效果?这种物理表现的核心就是绳索模拟技术。本文将揭秘通过Verlet积分实现实时绳索模拟的方案,并配合Cocos Creator进行实战演示。
本文以以往文章代码库
https://github.com/haiyoucuv/Wechat_article
涉及知识
- TypeScript
- CocosCreator3.x
- 代数几何
Verlet积分核心原理
相比传统欧拉法,Verlet积分通过位置差求速度:
速度 = 当前帧的位置 - 上一帧的位置
下一帧的位置 = 当前帧的位置 + 速度 * 步长
其他力的影响
这种方法的优势在于:
- 无需显式存储速度,减少状态变量
- 数值稳定性更好
- 能量守恒性质更好
约束求解
绳索的物理特性主要通过距离约束实现:
- 相邻节点间距保持固定
- 通过多次迭代调整位置满足约束
- 约束求解确保绳索不会过度拉伸
代码实现
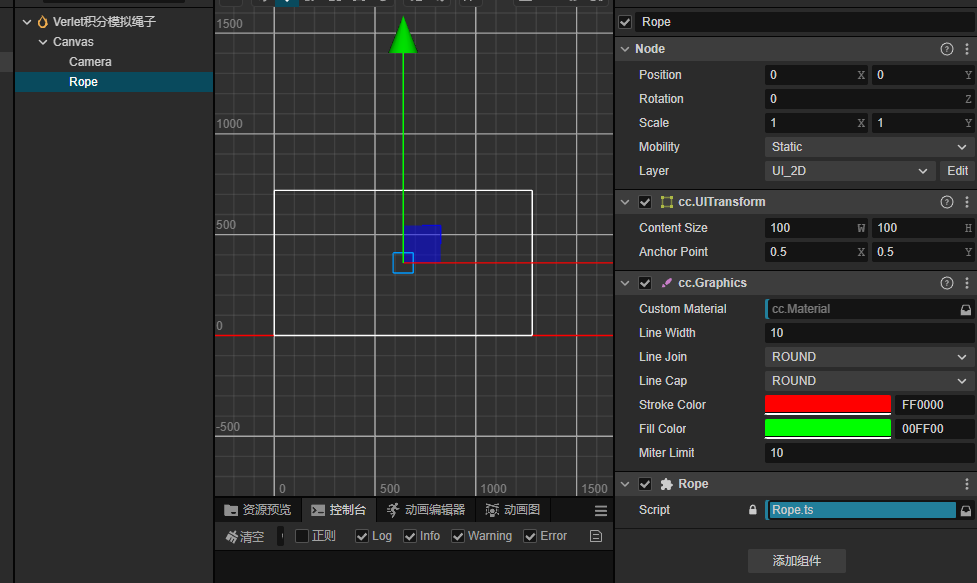
创建一个场景,并创建一个Rope脚本,场景中新建节点并添加Graphics组件,用于绘制绳索。
我们先实现一个节点类,和一个重力常量,包含位置、上一帧位置等状态变量。
然后创建出来进行测试
节点类定义
/**
* 重力
*/
const GRAVITY = new Vec2(0, -98);
class RopeNode {
/**
* 当前帧位置
*/
pos: Vec2 = null;
/**
* 上一帧的位置
*/
prePos: Vec2 = null;
constructor(x: number, y: number) {
this.pos = v2(x, y);
this.prePos = v2(x, y);
}
onUpdate(dt: number) {
// 计算速度(这个步长已经是两帧之间的步长了)
const v = Vec2.subtract(new Vec2(), this.pos, this.prePos);
// 保存上一帧的位置
this.prePos.set(this.pos);
// 叠加重力加速度
v.add(Vec2.multiplyScalar(new Vec2(), GRAVITY, dt));
// 计算下一帧位置
this.pos.add(v);
}
}
在脚本中创建出来进行测试
@ccclass('Rope')
export class Rope extends Component {
private graphics: Graphics = null;
point: RopeNode = null;
onLoad() {
this.graphics = this.node.getComponent(Graphics);
}
start() {
this.point = new RopeNode(0, 300);
}
/**
* 绘制
*/
draw() {
this.graphics.clear();
// 画出点
this.graphics.moveTo(this.point.pos.x, this.point.pos.y);
this.graphics.circle(this.point.pos.x, this.point.pos.y, 30);
this.graphics.fill();
}
/**
* 更新
* @param dt
*/
update(dt: number) {
this.point.onUpdate(dt);
}
}
我们可以看到这个节点加速移出屏幕外了,说明我们的代码是没问题的。
实现绳索
接下来我们实现一个完整的绳索类,包含节点数组、基础长度、节点数量等状态变量。
实现绳索的关键是实现节点间的约束求解,确保绳索的物理特性。
我们来实现一个简单的约束demo
绳索类核心逻辑
@ccclass('Rope')
export class Rope extends Component {
/**
* 节点数组
*/
nodeArr: RopeNode[] = [];
/**
* 头节点
*/
head: RopeNode = null;
/**
* 基础长度
*/
baseLen = 20;
/**
* 节点数量
*/
count = 30;
private graphics: Graphics = null;
onLoad() {
this.graphics = this.node.getComponent(Graphics);
input.on(Input.EventType.TOUCH_MOVE, this.onTouchMove, this);
}
start() {
// 初始化节点
for (let i = 0; i < this.count; i++) {
this.nodeArr.push(new RopeNode(0, 0));
}
this.head = this.nodeArr[0];
}
/**
* 鼠标事件,用于把头节点移到指定位置
*/
onTouchMove = (() => {
const tempPos = new Vec3();
return (e: EventTouch) => {
const uiPos = e.getUILocation();
tempPos.set(uiPos.x, uiPos.y, 0);
this.getComponent(UITransform).convertToNodeSpaceAR(tempPos, tempPos);
// 把头部移动到指定位置
this.head.pos.set(tempPos.x, tempPos.y);
}
})()
/**
* 更新节点
* @param dt
*/
updatePoints(dt: number) {
const { nodeArr } = this;
const len = nodeArr.length;
for (let i = 1; i < len; i++) {
const p = nodeArr[i];
p.onUpdate(dt);
}
}
/**
* 简单的约束
*/
constraint() {
const { nodeArr } = this;
// 多次迭代保证稳定性
const time = 20;
for (let step = 0; step < time; step++) {
const len = this.nodeArr.length - 1;
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
const p = nodeArr[i];
const next = nodeArr[i + 1];
// 相邻节点间距
const dp = Vec2.subtract(new Vec2(), p.pos, next.pos);
const dis = dp.length();
// 超出基础长度时调整位置
if (dis > this.baseLen) {
const delta = dis - this.baseLen;
const dir = dp.normalize().multiplyScalar(delta);
if (i !== 0) {
dir.multiplyScalar(0.5);
p.pos.subtract(dir);
next.pos.add(dir);
} else {
next.pos.add(dir);
}
}
}
}
}
/**
* 绘制
*/
draw() {
this.graphics.clear();
// 画出绳子
this.graphics.moveTo(this.head.pos.x, this.head.pos.y);
for (let i = 1; i < this.nodeArr.length; i++) {
const node = this.nodeArr[i];
this.graphics.lineTo(node.pos.x, node.pos.y);
}
this.graphics.stroke();
// 画出节点
for (let i = 0; i < this.nodeArr.length; i++) {
const node = this.nodeArr[i];
this.graphics.moveTo(node.pos.x, node.pos.y);
this.graphics.circle(node.pos.x, node.pos.y, 5);
this.graphics.fill();
}
}
/**
* 更新
* @param dt
*/
update(dt: number) {
this.updatePoints(dt);
this.constraint();
this.draw();
}
}
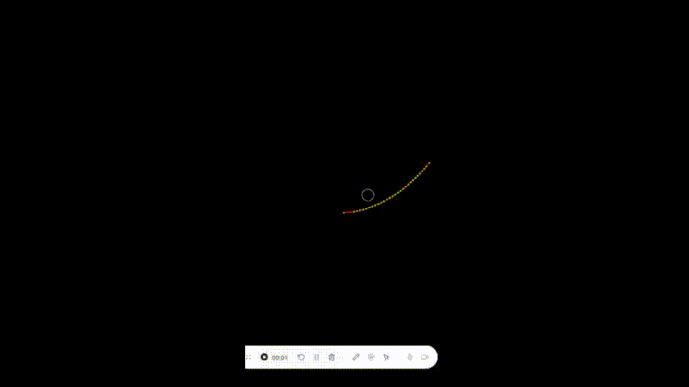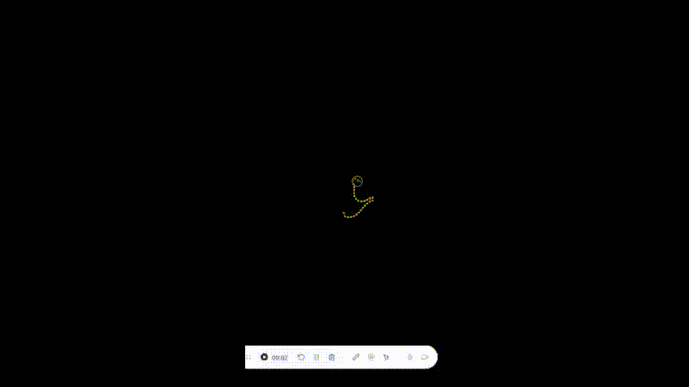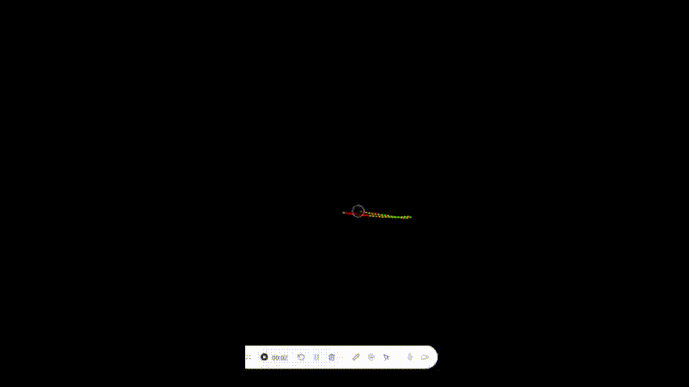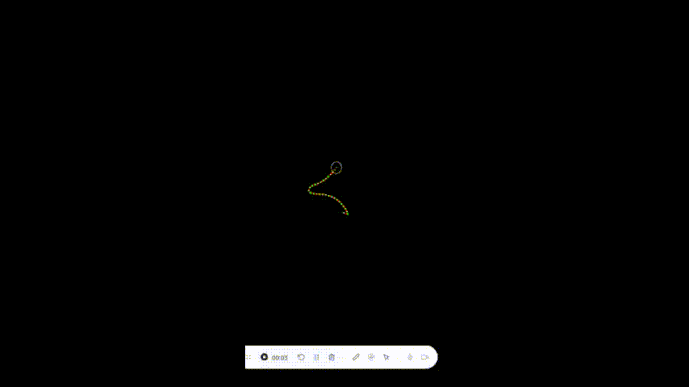
我们可以看到,这个demo已经实现了一个简单的绳索,我们可以通过鼠标移动头节点,来改变绳索的长度。
实现要点解析
1. 位置更新
速度计算
- 通过位置差计算速度:
v = pos - prePos - 无需显式存储速度状态变量
- 自动包含了上一帧的加速度影响
重力影响
- 重力加速度产生的位移:
Δv = g * dt - 可以通过调整重力系数控制下落速度
位置更新流程
- 保存当前位置到prePos
- 计算速度向量(pos - prePos)
- 应用重力加速度影响
- 更新节点新位置
2. 约束处理
- 检测相邻节点间距
- 超出基础长度时调整位置
- 多次迭代保证稳定性
3. 绘制渲染
- 使用Graphics组件绘制
- 连接节点形成绳索
- 可视化节点位置
应用场景
- 游戏物理:绳索、藤蔓、锁链等
- 布料模拟:旗帜、衣物等
- 特效制作:丝带、流苏等
相关代码在哪里
https://github.com/haiyoucuv/Wechat_article
结语
Verlet积分因其简单高效的特点,在游戏物理模拟中广受欢迎。本文介绍的绳索模拟方案,可以轻松实现逼真的物理效果,希望对你的游戏开发有所帮助。
点击上方码不了一点+关注和★ 星标