这是之前的帖子链接:2D 大风吹树效果求思路
以及我正在开坑的关联的单机游戏: Cocos Creator | Game_1
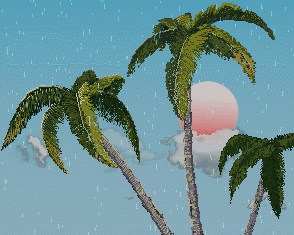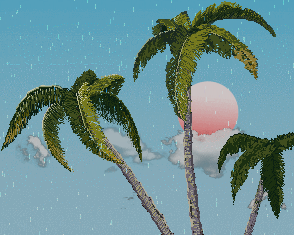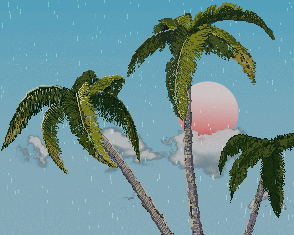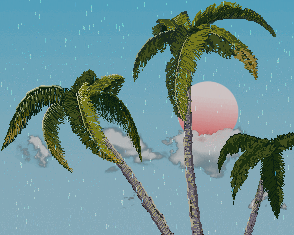
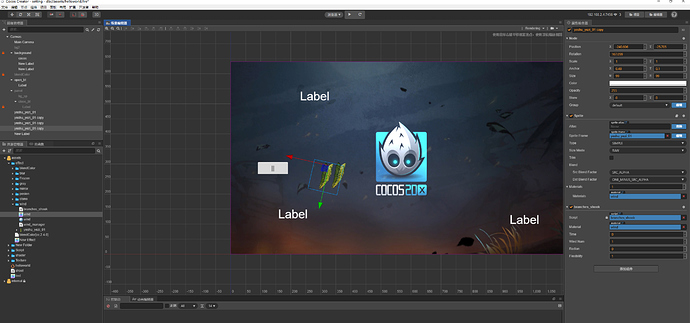
效果体验 链接:Cocos Creator | NewProject
问题1:要做什么?
观察树枝受风时的变化,我们看到 1. 树枝弯曲了 2.树枝在摆动

参考示例:CocosCreator Shader学习(四):花草摆动效果_三思而先行的博客-CSDN博客
shader 知识点 Cocos Creator Shader Effect 系列 - 1 - 材质,Effect,Inspector,纹理之间的关系 - 简书
问题2:如何制作?
分3个部分:
1.shader能使图片弯曲:
制作能够使图片弯曲的shader ,设置对弯曲程度可变的风力值参数
将shader设置给材质, 再将材质在树枝节点
2.树枝js脚本:能够控制节点角度变化
制作摆动风力函数sin函数, 设置对角度幅度变化的风力值参数
3.风力管理js
具体步骤:
1. 制作能够使图片弯曲的shader,设置对弯曲程度可变的风力值参数
//文件:sbranches_shook_Effect.effect
CCEffect %{
techniques:
- passes:
- vert: vs
frag: fs
blendState:
targets:
- blend: true
rasterizerState:
cullMode: none
properties:
texture: { value: white }
alphaThreshold: { value: 0.5 }
# time : {
# value: 0.0,
# editor: {
# tooltip: "时间"
# }
# }
wind_num: {
value: 1.0,
editor: {
tooltip: "风力值"
}
}
radian: {
value: 1.0,
editor: {
tooltip: "旋转值"
}
}
Flexibility: { value: 1.0,
editor: {
tooltip: "柔韧度,数值越大越容易弯曲"
}
}
value_1: {
value: 0.5,
editor: {
tooltip: "参数1"
}
}
value_2: {
value: 4.0,
editor: {
tooltip: "参数2"
}
}
}%
CCProgram vs %{
precision highp float;
#include <cc-global>
#include <cc-local>
in vec3 a_position;
in vec4 a_color;
out vec4 v_color;
#if USE_TEXTURE
in vec2 a_uv0;
out vec2 v_uv0;
#endif
void main () {
vec4 pos = vec4(a_position, 1);
#if CC_USE_MODEL
pos = cc_matViewProj * cc_matWorld * pos;
#else
pos = cc_matViewProj * pos;
#endif
#if USE_TEXTURE
v_uv0 = a_uv0;
#endif
v_color = a_color;
gl_Position = pos;
}
}%
CCProgram fs %{
precision highp float;
#include <alpha-test>
in vec4 v_color;
#if USE_TEXTURE
in vec2 v_uv0;
uniform sampler2D texture;
// uniform inputData{
// float time;
// };
uniform inputData1{
float wind_num;
};
uniform inputData2{
float radian;
};
uniform inputData3{
float Flexibility;
};
uniform inputData4{
float value_1;
};
uniform inputData5{
float value_2;
};
#endif
void main () {
vec4 o = vec4(1, 1, 1, 1);
// 风吹植物变形算法
// 一.脚本功能
// 1.风力大小,方向角度
// 2.材质柔韧性越小的,弯曲幅度越小
// 二.shader功能
// 1.表现弯曲方向一致,计算包含自身旋转
// 2.素材要求完整正方形,防止动画裁切
// 3.素材要求以底部为不动点,
// 根据自身角度计算 风向量,风力值决定了最大点偏移多少
float wind_x = -1.0 * wind_num * cos( radian );
//////////////////////// 弯曲算法: ____________________________
// 获取v_uv0这个点距离中心点的真实距离
float height = 1.0 - v_uv0.y;
// 使用pow函数,让距离中心点越长的地方摆动幅度越明显且成抛物线形态(中心点以下部位不参与偏移)
// x轴偏移量
float offset_x = value_1 * pow(height, value_2) * wind_x;
// x新的坐标
float new_x = v_uv0.x + offset_x;
// 通过三角函数,计算出Y轴偏移量
// y的新坐标
float offset_y = pow(offset_x, 2.0) * 2.0;
float new_y = v_uv0.y - offset_y;
////////////////////////风量抖动算法_____________________________
////////////////////////
#if USE_TEXTURE
// fract函数是GLSL内建函数,取小数部分
o *= texture(texture, fract(vec2(new_x, new_y)));
if(new_x <0.0 || new_x>1.0 || new_y<0.0){
o = vec4(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
}
#if CC_USE_ALPHA_ATLAS_TEXTURE
o.a *= texture2D(texture, v_uv0 + vec2(0, 0.5)).r;
#endif
#endif
o *= v_color;
ALPHA_TEST(o);
gl_FragColor = o;
}
}%
// 然后新建一个材质,设置材质的effect,为上面的文件

// 新建树枝图片节点 //注意::(被使用的图片需要 去掉图片素材packable ,否则有概率自动合图合图将错误计算uv)

// 将材质放到树枝
//树枝脚本:branches_shook.js
cc.Class({
extends: cc.Component,
properties: {
material: {
default: null,
type: cc.Material
},
time: {
default: 0
},
wind_num: {
default: 1,
tooltip: "风力值"
},
radian: {
default: 0,
tooltip: "旋转角度转弧度值"
},
Flexibility: {
default: 1,
tooltip: "柔韧度" // 柔韧度影响弯曲度
}
},
// LIFE-CYCLE CALLBACKS:
onLoad() {
this.set_raotaion();
},
start() {
this.material = this.node.getComponent(cc.Sprite).getMaterial(0);
},
update(dt) {
this.time += dt;
if (globalThis.WeatherManager) {
this.wind_num = globalThis.WeatherManager.wind_num;
}
if (this.node.active && this.material != null) {
this.radian = (this.node.angle) * Math.PI / 180;
// this.material.setProperty("time", this.time);
this.material.setProperty("wind_num", this.wind_num);
this.material.setProperty("radian", this.radian);
this.material.setProperty("Flexibility", this.Flexibility);
}
this.update_wind(dt);
},
// 树枝对风力值感受
// 1.树枝角度变形
set_raotaion: function () {
// 记录树枝的角度
this.angle = this.node.angle;
if (this.angle < 0) {
this.angle += 360;
}
this.time = Math.random() * 2;
},
// 2.根据风大小方向,动态抖动树叶角度,抖动树叶弯曲值1
update_wind: function (dt) {
this.time += dt;
// 根据时间值,计算出sin规律
var _num1 = Math.sin(this.time * (this.wind_num / 2));
// 计算出偏移角度
// if (this.wind_num > 0) {
if (this.angle > 90 && this.angle < 270) {
this.node.angle = this.angle + (this.wind_num * (_num1 + 1));
} else {
this.node.angle = this.angle - (this.wind_num * (_num1 + 1));
}
// }
// if (this.wind_num < 0) {
// if (this.angle > 90 && this.angle < 270) {
// this.node.angle = this.angle + (this.wind_num * (_num1 + 1) * 2);
// } else {
// this.node.angle = this.angle - (this.wind_num * (_num1 + 1) * 2);
// }
// }
// 计算出偏移抖动值1
this.material.setProperty("value_1", Math.abs(this.wind_num) * (_num1 + 1) * 0.02 + 0.1);
}
});
wind_manager.js
cc.Class({
extends: cc.Component,
properties: {
wind_num: 1,
wind_label: {
default: null,
type: cc.Label,
tooltip: "风力描述label"
}
},
// LIFE-CYCLE CALLBACKS:
onLoad() {
globalThis.WeatherManager = this;
},
start() {
},
update(dt) {
this.wind_label.string = "风力: " + this.wind_num;
},
on_change_wind: function (slider, customEventData) {
this.wind_num = slider.progress * 10 - 5;
}
});
设置一个滑动器,将风回调函数绑定到上面
最终效果:
为什么没有第一张图好看…emmmm, 那是…天气昼夜系统的效果

附上demo: NewProject.zip (1.3 MB)