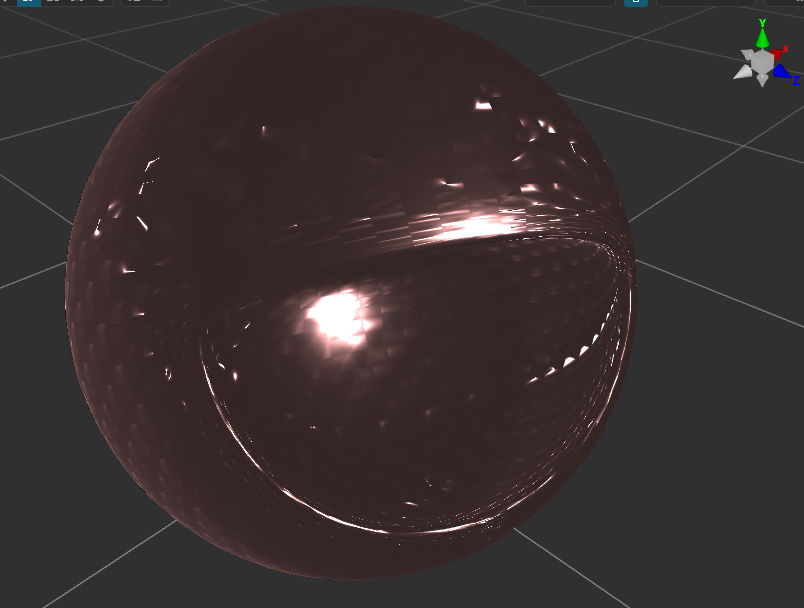
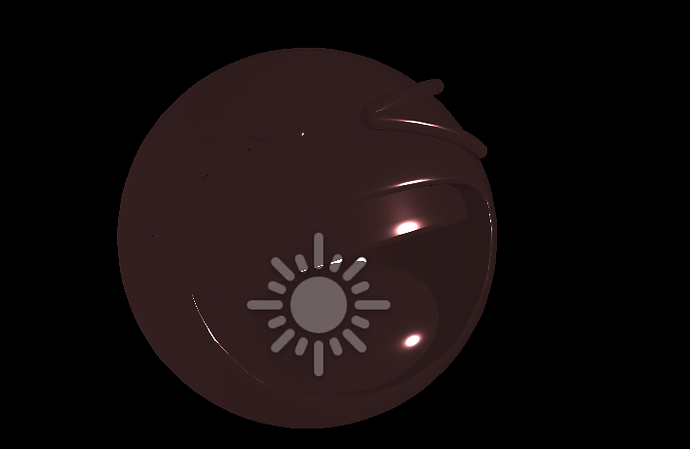
我在Cocos和Unity写了相同算法的Shader
在Cocos中表现:
代码
// Effect Syntax Guide: https://docs.cocos.com/creator/manual/zh/shader/index.html
CCEffect %{
techniques:
- name: opaque
passes:
- vert: general-vs:vert # builtin header
frag: disney-fs:frag
properties: &props
# mainTexture: { value: white }
mainColor: { value: [1, 1, 1, 1], editor: { type: color } }
metallic: { value: 0.0, editor: {slide: true, range: [0, 1.0], step: 0.01}}
subsurface: { value: 0.0, editor: {slide: true, range: [0, 1.0], step: 0.01}}
specular: { value: 0.5, editor: {slide: true, range: [0, 1.0], step: 0.01}}
roughness: { value: 0.5, editor: {slide: true, range: [0, 1.0], step: 0.01}}
specularTint: { value: 0.0, editor: {slide: true, range: [0, 1.0], step: 0.01}}
anisotropic: { value: 0.0, editor: {slide: true, range: [0, 1.0], step: 0.01}}
sheen: { value: 0.0, editor: {slide: true, range: [0, 1.0], step: 0.01}}
sheenTint: { value: 0.5, editor: {slide: true, range: [0, 1.0], step: 0.01}}
clearcoat: { value: 0.0, editor: {slide: true, range: [0, 1.0], step: 0.01}}
clearcoatGloss: { value: 1.0, editor: {slide: true, range: [0, 1.0], step: 0.01}}
}%
CCProgram disney-fs %{
precision highp float;
#include <builtin/uniforms/cc-global>
#include <legacy/output>
#include <legacy/fog-fs>
in vec2 v_uv;
in vec3 v_normal;
in vec3 v_position;
in vec3 v_tangent;
in vec3 v_bitangent;
uniform sampler2D mainTexture;
const float PI = 3.14159265358979323846;
uniform Constant {
vec4 mainColor;
float metallic;
float subsurface;
float specular;
float roughness;
float specularTint;
float anisotropic;
float sheen;
float sheenTint;
float clearcoat;
float clearcoatGloss;
};
float sqr(float x) { return x*x; }
float SchlickFresnel(float u)
{
float m = clamp(1.0-u, 0.0, 1.0);
float m2 = m*m;
return m2*m2*m; // pow(m,5)
}
float GTR1(float NdotH, float a)
{
if (a >= 1.0) return 1.0/PI;
float a2 = a*a;
float t = 1.0 + (a2-1.0)*NdotH*NdotH;
return (a2-1.0) / (PI*log(a2)*t);
}
float GTR2(float NdotH, float a)
{
float a2 = a*a;
float t = 1.0 + (a2-1.0)*NdotH*NdotH;
return a2 / (PI * t*t);
}
float GTR2_aniso(float NdotH, float HdotX, float HdotY, float ax, float ay)
{
return 1.0 / (PI * ax*ay * sqr( sqr(HdotX/ax) + sqr(HdotY/ay) + NdotH*NdotH ));
}
float smithG_GGX(float NdotV, float alphaG)
{
float a = alphaG*alphaG;
float b = NdotV*NdotV;
return 1.0 / (NdotV + sqrt(a + b - a*b));
}
float smithG_GGX_aniso(float NdotV, float VdotX, float VdotY, float ax, float ay)
{
return 1.0 / (NdotV + sqrt( sqr(VdotX*ax) + sqr(VdotY*ay) + sqr(NdotV) ));
}
vec3 mon2lin(vec3 x)
{
return vec3(pow(x[0], 2.2), pow(x[1], 2.2), pow(x[2], 2.2));
}
vec3 BRDF( vec3 L, vec3 V, vec3 N, vec3 X, vec3 Y )
{
// 法线和光线的夹角
float NdotL = max(dot(N,L), 0.0);
// 法线和视线的夹角
float NdotV = max(dot(N,V), 0.0);
// 半角向量
vec3 H = normalize(L+V);
float NdotH = max(dot(N,H), 0.0);
float LdotH = max(dot(L,H), 0.0);
vec3 Cdlin = mon2lin(mainColor.rgb);
float Cdlum = .3*Cdlin[0] + .6*Cdlin[1] + .1*Cdlin[2]; // luminance approx.
vec3 Ctint = Cdlum > 0.0 ? Cdlin/Cdlum : vec3(1.0,1.0,1.0); // normalize lum. to isolate hue+sat
vec3 Cspec0 = mix(specular*.08*mix(vec3(1.0,1.0,1.0), Ctint, specularTint), Cdlin, metallic);
vec3 Csheen = mix(vec3(1.0,1.0,1.0), Ctint, sheenTint);
// Diffuse fresnel - go from 1 at normal incidence to .5 at grazing
// and mix in diffuse retro-reflection based on roughness
float FL = SchlickFresnel(NdotL), FV = SchlickFresnel(NdotV);
float Fd90 = 0.5 + 2.0 * LdotH * LdotH * roughness;
float Fd = mix(1.0, Fd90, FL) * mix(1.0, Fd90, FV);
// Based on Hanrahan-Krueger brdf approximation of isotropic bssrdf
// 1.25 scale is used to (roughly) preserve albedo
// Fss90 used to "flatten" retroreflection based on roughness
float Fss90 = LdotH*LdotH*roughness;
float Fss = mix(1.0, Fss90, FL) * mix(1.0, Fss90, FV);
float ss = 1.25 * (Fss * (1.0 / (NdotL + NdotV) - .5) + .5);
// specular
float aspect = sqrt(1.0-anisotropic*.9);
float ax = max(.001, sqr(roughness)/aspect);
float ay = max(.001, sqr(roughness)*aspect);
float Ds = GTR2_aniso(NdotH, dot(H, X), dot(H, Y), ax, ay);
float FH = SchlickFresnel(LdotH);
vec3 Fs = mix(Cspec0, vec3(1.0,1.0,1.0), FH);
float Gs = smithG_GGX_aniso(NdotL, dot(L, X), dot(L, Y), ax, ay);
Gs *= smithG_GGX_aniso(NdotV, dot(V, X), dot(V, Y), ax, ay);
// sheen
vec3 Fsheen = FH * sheen * Csheen;
// clearcoat (ior = 1.5 -> F0 = 0.04)
float Dr = GTR1(NdotH, mix(.1,.001,clearcoatGloss));
float Fr = mix(.04, 1.0, FH);
float Gr = smithG_GGX(NdotL, .25) * smithG_GGX(NdotV, .25);
return (mix(Fd, ss, subsurface)*Cdlin + Fsheen) * (1.0-metallic)+ Gs*Fs*Ds + .25*clearcoat*Gr*Fr*Dr;
}
vec4 frag () {
// 光源方向
vec3 lightDirection = normalize(-cc_mainLitDir.xyz);
// 视线方向
vec3 viewDirection = normalize(cc_cameraPos.xyz - v_position);
// 法线方向
vec3 normalDirection = normalize(v_normal);
vec3 worldTangent = normalize(v_tangent);
vec3 worldBinormal = normalize(v_bitangent);
return vec4(BRDF(lightDirection, viewDirection, normalDirection, worldTangent, worldBinormal), 1.0);
}
}%
在Unity中表现:
代码:
Shader "Disney"
{
Properties
{
baseColor("Base Color",Color)=(1,1,1,1)
metallic ("Metallic", Range (0.0,1.0)) = 0.0
subsurface ("Subsurface", Range (0.0,1.0)) = 0.0
_specular ("Specular", Range (0.0,1.0)) = 0.0
roughness ("Roughness", Range (0.0,1.0)) = 0.5
specularTint ("SpecularTint", Range (0.0,1.0)) = 0.0
anisotropic ("Anisotropic", Range (0.0,1.0)) = 0.0
sheen ("Sheen", Range (0.0,1.0)) = 0.0
sheenTint ("SheenTint", Range (0.0,1.0)) = 0.5
clearcoat ("Clearcoat", Range (0.0,1.0)) = 0.0
clearcoatGloss ("ClearcoatGloss", Range (0.0,1.0)) = 1.0
}
SubShader
{
Pass
{
CGPROGRAM
#pragma vertex VSMain
#pragma fragment PSMain
float3 baseColor;
float metallic, subsurface, _specular, roughness, specularTint, anisotropic, sheen,
sheenTint, clearcoat, clearcoatGloss;
static const float PI = 3.14159265358979323846;
float sqr(float x) { return x*x; }
float SchlickFresnel(float u)
{
float m = clamp(1.0-u, 0.0, 1.0);
float m2 = m*m;
return m2*m2*m; // pow(m,5)
}
float GTR1(float NdotH, float a)
{
if (a >= 1.0) return 1.0/PI;
float a2 = a*a;
float t = 1.0 + (a2-1.0)*NdotH*NdotH;
return (a2-1.0) / (PI*log(a2)*t);
}
float GTR2(float NdotH, float a)
{
float a2 = a*a;
float t = 1.0 + (a2-1.0)*NdotH*NdotH;
return a2 / (PI * t*t);
}
float GTR2_aniso(float NdotH, float HdotX, float HdotY, float ax, float ay)
{
return 1.0 / (PI * ax*ay * sqr( sqr(HdotX/ax) + sqr(HdotY/ay) + NdotH*NdotH ));
}
float smithG_GGX(float NdotV, float alphaG)
{
float a = alphaG*alphaG;
float b = NdotV*NdotV;
return 1.0 / (NdotV + sqrt(a + b - a*b));
}
float smithG_GGX_aniso(float NdotV, float VdotX, float VdotY, float ax, float ay)
{
return 1.0 / (NdotV + sqrt( sqr(VdotX*ax) + sqr(VdotY*ay) + sqr(NdotV) ));
}
float3 mon2lin(float3 x)
{
return float3(pow(x[0], 2.2), pow(x[1], 2.2), pow(x[2], 2.2));
}
float3 BRDF( float3 L, float3 V, float3 N, float3 X, float3 Y )
{
float NdotL = max(dot(N,L),0.0);
float NdotV = max(dot(N,V),0.0);
float3 H = normalize(L+V);
float NdotH = max(dot(N,H),0.0);
float LdotH = max(dot(L,H),0.0);
float3 Cdlin = mon2lin(baseColor);
float Cdlum = .3*Cdlin[0] + .6*Cdlin[1] + .1*Cdlin[2]; // luminance approx.
float3 Ctint = Cdlum > 0.0 ? Cdlin/Cdlum : float3(1.0,1.0,1.0); // normalize lum. to isolate hue+sat
float3 Cspec0 = lerp(_specular*.08*lerp(float3(1.0,1.0,1.0), Ctint, specularTint), Cdlin, metallic);
float3 Csheen = lerp(float3(1.0,1.0,1.0), Ctint, sheenTint);
// Diffuse fresnel - go from 1 at normal incidence to .5 at grazing
// and lerp in diffuse retro-reflection based on roughness
float FL = SchlickFresnel(NdotL), FV = SchlickFresnel(NdotV);
float Fd90 = 0.5 + 2.0 * LdotH*LdotH * roughness;
float Fd = lerp(1.0, Fd90, FL) * lerp(1.0, Fd90, FV);
// Based on Hanrahan-Krueger brdf approximation of isotropic bssrdf
// 1.25 scale is used to (roughly) preserve albedo
// Fss90 used to "flatten" retroreflection based on roughness
float Fss90 = LdotH*LdotH*roughness;
float Fss = lerp(1.0, Fss90, FL) * lerp(1.0, Fss90, FV);
float ss = 1.25 * (Fss * (1.0 / (NdotL + NdotV) - .5) + .5);
// specular
float aspect = sqrt(1.0-anisotropic*.9);
float ax = max(.001, sqr(roughness)/aspect);
float ay = max(.001, sqr(roughness)*aspect);
float Ds = GTR2_aniso(NdotH, dot(H, X), dot(H, Y), ax, ay);
float FH = SchlickFresnel(LdotH);
float3 Fs = lerp(Cspec0, float3(1.0,1.0,1.0), FH);
float Gs = smithG_GGX_aniso(NdotL, dot(L, X), dot(L, Y), ax, ay);
Gs *= smithG_GGX_aniso(NdotV, dot(V, X), dot(V, Y), ax, ay);
// sheen
float3 Fsheen = FH * sheen * Csheen;
// clearcoat (ior = 1.5 -> F0 = 0.04)
float Dr = GTR1(NdotH, lerp(.1,.001,clearcoatGloss));
float Fr = lerp(.04, 1.0, FH);
float Gr = smithG_GGX(NdotL, .25) * smithG_GGX(NdotV, .25);
return (lerp(Fd, ss, subsurface)*Cdlin + Fsheen) * (1.0-metallic) + Gs*Fs*Ds + .25*clearcoat*Gr*Fr*Dr;
}
void VSMain (inout float4 vertex:POSITION, inout float2 uv:TEXCOORD0, inout float3 normal:NORMAL, inout float4 tangent:TANGENT, out float3 world:TEXCOORD1)
{
world = mul(unity_ObjectToWorld, vertex).xyz;
vertex = UnityObjectToClipPos(vertex);
}
float4 PSMain (float4 vertex:POSITION, float2 uv:TEXCOORD0, float3 normal:NORMAL, float4 tangent:TANGENT, float3 world:TEXCOORD1) : SV_TARGET
{
float3 LightDirection = normalize(lerp(_WorldSpaceLightPos0.xyz, _WorldSpaceLightPos0.xyz - world, _WorldSpaceLightPos0.w));
float3 NormalDirection = normalize(mul((float3x3)unity_ObjectToWorld,normal));
float3 ViewDirection = normalize(_WorldSpaceCameraPos.xyz - world);
float3 WorldTangent = mul((float3x3)unity_ObjectToWorld,tangent.xyz);
float3 WorldBinormal = cross(NormalDirection,WorldTangent)*tangent.w;
return float4(BRDF( LightDirection, ViewDirection, NormalDirection, WorldTangent, WorldBinormal), 1.0);
}
ENDCG
}
}
}
在Unity中显示的是光滑平整的,在Cocos中显示的有棱角
测试中发现与 v_tangent 和 v_bitangent两个切线向量有关。
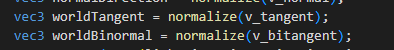
请问下Cocos 和 Unity的切线向量有区别吗