目前使用的是98k大佬的碰撞检测系统,没有使用碰撞体,也就没有射线,那如何实现这条线碰撞到障碍物会发生反射呢
我现在想预测球的运动轨迹,碰到障碍物会反射的那种。
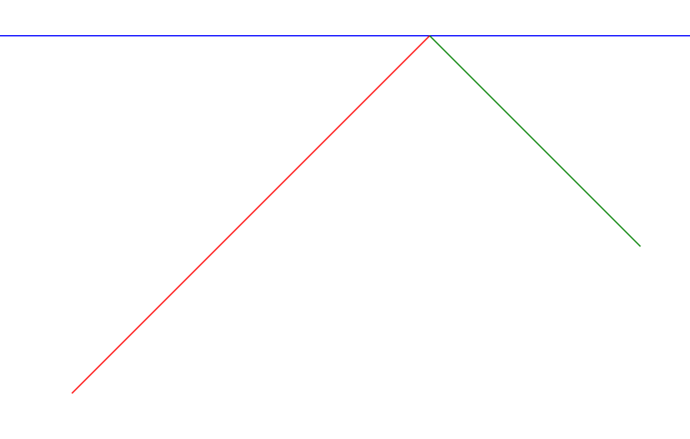
45度角射入墙角会有惊喜
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Light Reflection</title>
<style>
canvas {
border: 1px solid black;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<canvas id="canvas" width="1280" height="960"></canvas>
<script>
const canvas = document.getElementById('canvas');
const ctx = canvas.getContext('2d');
// 将左下角设为原点
ctx.translate(0, canvas.height);
ctx.scale(1, -1);
// 光线的起点和方向
const startX = 200;
const startY = 200;
const angle = Math.PI / 2/2; // 45度
const directionX = Math.cos(angle);
const directionY = Math.sin(angle);
// 镜面的位置
const mirrorY = 800;
// 计算碰撞点
const t = (mirrorY - startY) / directionY;
const collisionX = startX + t * directionX;
const collisionY = mirrorY;
// 法线向量
const normalX = 0;
const normalY = 1;
// 计算反射方向
const dotProduct = directionX * normalX + directionY * normalY;
const reflectX = directionX - 2 * dotProduct * normalX;
const reflectY = directionY - 2 * dotProduct * normalY;
// console.log("计算反射方向", dotProduct, reflectX, reflectY);
// 绘制函数
function draw() {
ctx.clearRect(0, 0, canvas.width, canvas.height);
// 绘制坐标系
drawAxis();
// 绘制镜面
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(0, mirrorY);
ctx.lineTo(canvas.width, mirrorY);
ctx.strokeStyle = 'blue';
ctx.lineWidth = 2;
ctx.stroke();
// 绘制入射光线
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(startX, startY);
ctx.lineTo(collisionX, collisionY);
ctx.strokeStyle = 'red';
ctx.lineWidth = 2;
ctx.stroke();
// 绘制反射光线
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(collisionX, collisionY);
ctx.lineTo(collisionX + reflectX * 500, collisionY + reflectY * 500); // 延长反射光线
ctx.strokeStyle = 'green';
ctx.lineWidth = 2;
ctx.stroke();
}
// 绘制坐标系
function drawAxis() {
// 绘制 X 轴
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(0, 0);
ctx.lineTo(canvas.width, 0);
ctx.strokeStyle = 'black';
ctx.lineWidth = 1;
ctx.stroke();
// 绘制 Y 轴
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(0, 0);
ctx.lineTo(0, canvas.height);
ctx.strokeStyle = 'black';
ctx.lineWidth = 1;
ctx.stroke();
// 绘制刻度
const step = 50;
ctx.font = '12px Arial';
ctx.fillStyle = 'black';
for (let i = step; i < canvas.width; i += step) {
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(i, -5);
ctx.lineTo(i, 5);
ctx.stroke();
ctx.fillText(i, i - 10, -10);
}
for (let i = step; i < canvas.height; i += step) {
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(-5, i);
ctx.lineTo(5, i);
ctx.stroke();
ctx.fillText(i, 10, i + 5);
}
}
// 初始化绘制
draw();
function asyncOperation() {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
const success = Math.random() > 0.5;
if (success) {
resolve('操作成功11111111');
} else {
reject('操作失败000000000');
}
}, 1000);
});
}
asyncOperation().then((res) => {
// console.log(res)
}, (res) => {
// console.log(res)
})
// reportError("D")
const myPromise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
console.log('A');
for (let index = 0; index < 100; index++) {
const element = Math.random()
if (element === 0) {
console.log("D")
resolve('B');
}
}
// reject("H")
reject(new Error('操作失败'));
});
console.log('C');
myPromise.then(result => {
console.log(result); // 输出 resolve
}, (result) => {
console.log(result);
}).catch(error => {
console.error(error);
});
const worker = new Worker('worker.js');
// function print(delay, message) {
// return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
// setTimeout(function () {
// console.log(message);
// resolve();
// }, delay);
// });
// }
// async function asyncFunc() {
// await print(1000, "First");
// await print(4000, "Second");
// await print(3000, "Third");
// }
// asyncFunc();
</script>
</body>
</html>
1赞
你发一个透明球,和那个真球一样的逻辑,但是一帧内就完成了n个 update 逻辑,碰撞时跳出循环,或者经过固定长度的路程就跳出循环。记录下路径,然后去渲染各个点。完全复用了之前的逻辑,计算结果和你碰撞一致,省时省力。
1赞
用射线拿法线,
或者碰撞位置修正方向做法线,你才能做反弹,
反射延长线,通常都是用时间去切片模拟位置,又或者射线连续反射
最后:万事有AI,这类问题, 它非常懂行,无论是修改或者扩展都能搞
射线检测加绘制组件来搞,
45度角入射,临界值处理好,就等于原路返回,应该没什么太大问题吧,
射入90度夹角 有可能会变成乒乓球