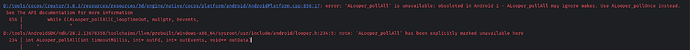Cocos v3.8.3 和 v 3.8.5版本
官方文档( 构建支持 16 KB 设备的 Android 应用)
https://developer.android.com/guide/practices/page-sizes?hl=zh-cn#update-packaging
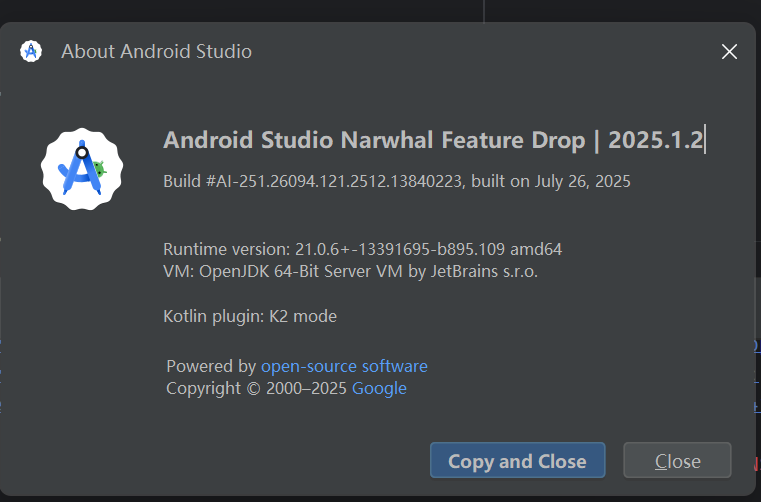
1、Android Studio 更新到:2025.1.2(按官方文档要求更新到对应版本即可)
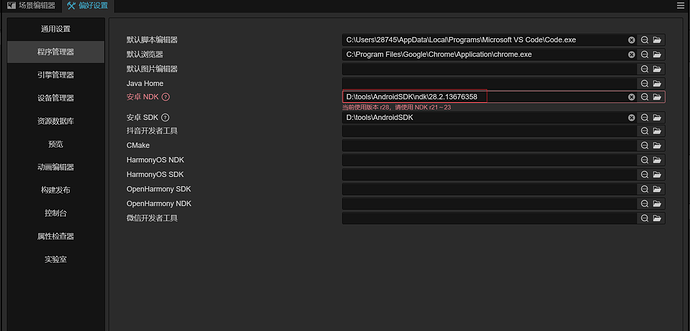
2、NDK 升级到: 28.2.13676358 (按官方文档要求更新到对应版本即可)
(1) Cocos红字提示部分不用管
(2) native\engine\android\app\build.gradle 中添加 ndkVersion 依赖项:
android {
ndkVersion “28.2.13676358”
compileSdkVersion PROP_COMPILE_SDK_VERSION.toInteger()
buildToolsVersion PROP_TARGET_SDK_VERSION
ndkPath PROP_NDK_PATH
namespace APPLICATION_ID
.
.
.
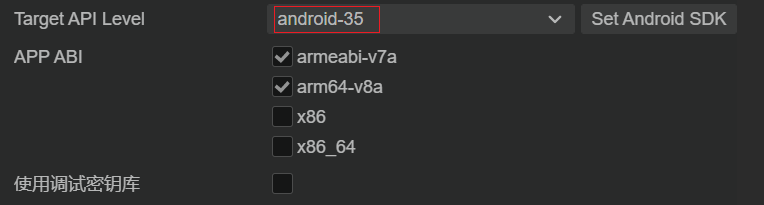
3、Android API 已更新到 35(这个很早就已经更新适配了)
4、接下来先构建打包 v3.8.3 版本:
(1) 构建报错1:while ((ALooper_pollAll(_loopTimeOut, nullptr, &events,
解决方案: * NDK 28 变更:ALooper_pollAll 被标注 unavailable(可能忽略唤醒),需改用 ALooper_pollOnce。
源码:
while ((ALooper_pollOnce(_loopTimeOut, nullptr, &events,
reinterpret_cast<void **>(&source))) >= 0) {
// process event
if (source != nullptr) {
source->process(_app, source);
}
// Exit the game loop when the Activity is destroyed
if (_app->destroyRequested) {
break;
}
}
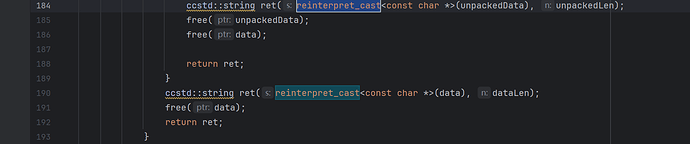
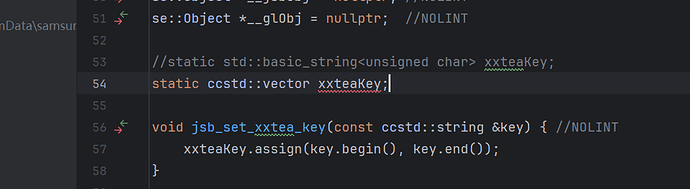
(2)构建报错2: xxteaKey.assign(key.begin(), key.end());
(3)构建报错3:const_cast<unsigned char *>(xxteaKey.data()),
jsb_global_init.cpp 文件
解决方案:
1)引入向量容器头文件(Cocos 包装或标准任一都可)
#include “base/std/container/vector.h”
2)static ccstd::vector xxteaKey;
源码位置:
// 原来
//static std::basic_string xxteaKey;
// 替换为
static ccstd::vector xxteaKey;
void jsb_set_xxtea_key(const ccstd::string &key) { //NOLINT
xxteaKey.assign(key.begin(), key.end());
}
3)改两处 xxtea_decrypt 调用参数(删除 const_cast/reinterpret_cast):
uint8_t *data = xxtea_decrypt(fileData.getBytes(),
static_cast<uint32_t>(fileData.getSize()),
xxteaKey.data(),
static_cast<uint32_t>(xxteaKey.size()),
reinterpret_cast<uint32_t *>(&dataLen));
以及
uint8_t *data = xxtea_decrypt(static_cast<uint8_t *>(fileData.getBytes()),
static_cast<uint32_t>(fileData.getSize()),
xxteaKey.data(),
static_cast<uint32_t>(xxteaKey.size()),
&dataLen);
5、替换 V8
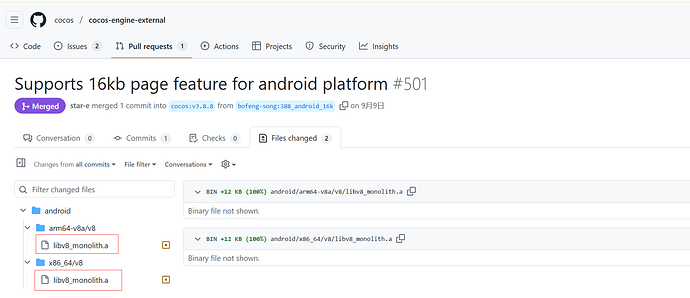
(1) 下载官方给的支持16KB的cocos-engine-external:
https://github.com/cocos/cocos-engine-external/tree/v3.8.8
(2) 将下载后的 D:\downloads\cocos-engine-external-3.8.8\android 中如图所示两个文件替换到本地对应的引擎位置:D:\tools\cocos\Creator\3.8.3\resources\resources\3d\engine-native\external\android
更新 arm64-v8a & x86_64 下的libv8_monolith.a
6、适配 V8
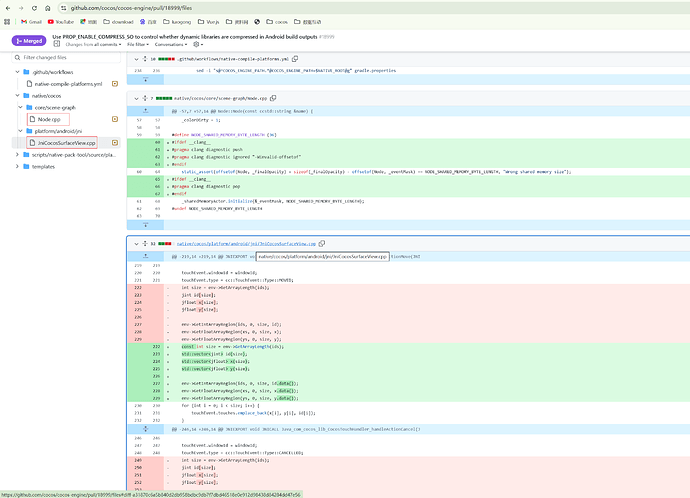
(1) cocos 官方修改 PR
如图两个文件修改
native/cocos/core/scene-graph/Node.cpp
native/cocos/platform/android/jni/JniCocosSurfaceView.cpp
(2) 本地引擎 Node.cpp
53 行左右,修改后的代码如下:
#define NODE_SHARED_MEMORY_BYTE_LENGTH (20)
#ifdef clang
#pragma clang diagnostic push
#pragma clang diagnostic ignored “-Winvalid-offsetof”
#endif
static_assert(offsetof(Node, _padding) + sizeof(_padding) - offsetof(Node, _eventMask) == NODE_SHARED_MEMORY_BYTE_LENGTH, “Wrong shared memory size”);
#ifdef clang
#pragma clang diagnostic pop
#endif
_sharedMemoryActor.initialize(&_eventMask, NODE_SHARED_MEMORY_BYTE_LENGTH);
#undef NODE_SHARED_MEMORY_BYTE_LENGTH
_id = idGenerator.getNewId();
if (name.empty()) {
_name.append("New Node");
} else {
_name = name;
}
// _eventProcessor = ccnew NodeEventProcessor(this);
}
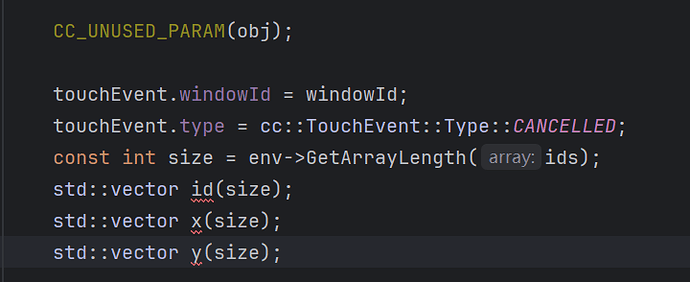
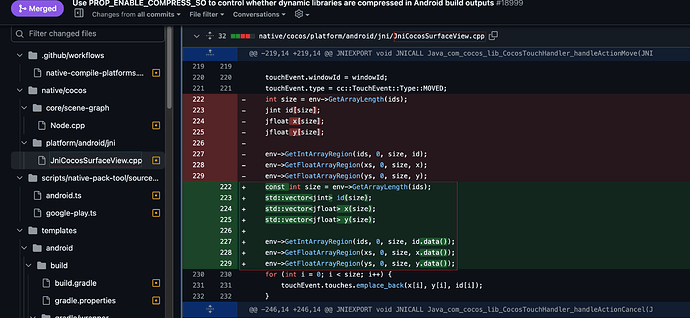
(3) 本地引擎 JniCocosSurfaceView.cpp
212行左右,修改后的代码如下:
touchEvent.windowId = windowId;
touchEvent.type = cc::TouchEvent::Type::MOVED;
const int size = env->GetArrayLength(ids);
std::vector<jint> id(size);
std::vector<jfloat> x(size);
std::vector<jfloat> y(size);
env->GetIntArrayRegion(ids, 0, size, id.data());
env->GetFloatArrayRegion(xs, 0, size, x.data());
env->GetFloatArrayRegion(ys, 0, size, y.data());
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
touchEvent.touches.emplace_back(x[i], y[i], id[i]);
}
249行左右:
touchEvent.windowId = windowId;
touchEvent.type = cc::TouchEvent::Type::CANCELLED;
const int size = env->GetArrayLength(ids);
std::vector id(size);
std::vector x(size);
std::vector y(size);
env->GetIntArrayRegion(ids, 0, size, id.data());
env->GetFloatArrayRegion(xs, 0, size, x.data());
env->GetFloatArrayRegion(ys, 0, size, y.data());
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
touchEvent.touches.emplace_back(x[i], y[i], id[i]);
}
6、构建打包 .apk 进行验证
(1) 使用 python 脚本进行验证,参考的该研发者的内容:
https://blog.csdn.net/gpf1320253667/article/details/151322842
(2) 安装并初始化 color 处理库,让 Windows 正确解析 ANSI:
pip install colorama
(3) 完整 python 脚本内容如下:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
-- coding: utf-8 --
“”"
check_page_alignment_windows.py
A Windows-friendly script (pure Python) that replicates the behavior of the Bash script:
-
Works on .so files directly
-
Works on directories (recursively finds *.so)
-
Works on .apk files by extracting and scanning embedded *.so files
It does NOT require objdump or unzip; it parses ELF headers and APKs with zipfile.
“”"
import os
import sys
import math
import struct
import tempfile
import zipfile
import argparse
from pathlib import Path
from typing import List, Tuple, Optional
============================= Colors / UI ====================================
try:
import colorama
colorama.just_fix_windows_console()
except Exception:
pass
ANSI colors (Windows 10+ supports these in most terminals; otherwise they’ll show raw codes)
RED = “\033[0;31m”
GREEN = “\033[0;32m”
BLUE = “\033[0;34m”
YELLOW= “\033[1;33m”
NC = “\033[0m”
def hrule(width: int = 120) -> str:
return "=" * width
def print_table_header():
print(f"{BLUE}{'Status':<8} {'File Path':<50} {'Architecture':<12} {'Alignment':<12} {'Notes'}{NC}")
print(hrule())
def print_table_row(symbol: str, filepath: str, arch: str, alignment: str, notes: str):
color = GREEN if symbol == "✅" else RED if symbol == "❌" else NC
print(f"{color}{symbol:<8}{NC} {filepath:<50} {arch:<12} {alignment:<12} {notes}")
============================= ELF parsing ====================================
ELF_MAGIC = b"\x7fELF"
ELFCLASS32 = 1
ELFCLASS64 = 2
ELFDATA2LSB = 1
ELFDATA2MSB = 2
PT_LOAD = 1
e_machine values
EM_386 = 3
EM_ARM = 40
EM_X86_64 = 62
EM_AARCH64 = 183
def arch_name(e_machine: int) -> str:
if e_machine == EM_AARCH64:
return "ARM64"
if e_machine == EM_X86_64:
return "x86_64"
if e_machine == EM_386:
return "x86"
if e_machine == EM_ARM:
return "ARM v7"
return "unknown"
def read_elf_info(path: str) -> Tuple[Optional[int], Optional[int], Optional[int], Optional[int], Optional[int]]:
"""
Returns (elf_class, data_encoding, e_machine, e_phoff, e_phnum) or (None,... ) if not ELF.
"""
with open(path, "rb") as f:
head = f.read(64) # enough for both 32/64 headers
if len(head) < 16 or head[:4] != ELF_MAGIC:
return (None, None, None, None, None)
elf_class = head[4]
data_enc = head[5] # 1 little, 2 big
# e_machine is at offset 18 (0x12), 2 bytes
if data_enc == ELFDATA2LSB:
e_machine = struct.unpack_from("<H", head, 18)[0]
elif data_enc == ELFDATA2MSB:
e_machine = struct.unpack_from(">H", head, 18)[0]
else:
return (None, None, None, None, None)
# e_phoff, e_phentsize, e_phnum differ by class
if elf_class == ELFCLASS32:
# Offsets: e_phoff @ 0x1C (4), e_phentsize @ 0x2A (2), e_phnum @ 0x2C (2)
f.seek(0)
ehdr = f.read(52) # 32-bit ELF header size
if data_enc == ELFDATA2LSB:
e_phoff = struct.unpack_from("<I", ehdr, 0x1C)[0]
e_phentsize = struct.unpack_from("<H", ehdr, 0x2A)[0]
e_phnum = struct.unpack_from("<H", ehdr, 0x2C)[0]
else:
e_phoff = struct.unpack_from(">I", ehdr, 0x1C)[0]
e_phentsize = struct.unpack_from(">H", ehdr, 0x2A)[0]
e_phnum = struct.unpack_from(">H", ehdr, 0x2C)[0]
elif elf_class == ELFCLASS64:
# Offsets: e_phoff @ 0x20 (8), e_phentsize @ 0x36 (2), e_phnum @ 0x38 (2)
f.seek(0)
ehdr = f.read(64) # 64-bit ELF header size
if data_enc == ELFDATA2LSB:
e_phoff = struct.unpack_from("<Q", ehdr, 0x20)[0]
e_phentsize = struct.unpack_from("<H", ehdr, 0x36)[0]
e_phnum = struct.unpack_from("<H", ehdr, 0x38)[0]
else:
e_phoff = struct.unpack_from(">Q", ehdr, 0x20)[0]
e_phentsize = struct.unpack_from(">H", ehdr, 0x36)[0]
e_phnum = struct.unpack_from(">H", ehdr, 0x38)[0]
else:
return (None, None, None, None, None)
return (elf_class, data_enc, e_machine, e_phoff, e_phnum)
def max_load_align_exponent(path: str) -> Optional[int]:
"""
Iterate program headers and return max log2(p_align) for PT_LOAD segments.
If p_align is 0, treat as 0 (i.e., 2**0).
"""
info = read_elf_info(path)
if info[0] is None:
return None
elf_class, data_enc, e_machine, e_phoff, e_phnum = info
if e_phoff is None or e_phnum is None:
return None
# Program header entry sizes:
if elf_class == ELFCLASS32:
# p_type(4), p_offset(4), p_vaddr(4), p_paddr(4), p_filesz(4), p_memsz(4), p_flags(4), p_align(4)
ph_size = 32
if data_enc == ELFDATA2LSB:
fmt = "<IIIIIIII"
else:
fmt = ">IIIIIIII"
p_type_idx = 0
p_align_idx = 7
else:
# 64-bit: p_type(4), p_flags(4), p_offset(8), p_vaddr(8), p_paddr(8), p_filesz(8), p_memsz(8), p_align(8)
ph_size = 56
if data_enc == ELFDATA2LSB:
fmt = "<IIQQQQQQ"
else:
fmt = ">IIQQQQQQ"
p_type_idx = 0
p_align_idx = 7
max_exp = None
with open(path, "rb") as f:
f.seek(e_phoff)
for _ in range(e_phnum):
data = f.read(ph_size)
if len(data) != ph_size:
break
fields = struct.unpack(fmt, data)
p_type = fields[p_type_idx]
if p_type == PT_LOAD:
p_align = fields[p_align_idx]
if p_align == 0:
exp = 0
else:
# p_align can be any number; compute floor(log2(p_align))
exp = int(math.log2(p_align)) if p_align > 0 else 0
max_exp = exp if max_exp is None else max(max_exp, exp)
return max_exp
def get_arch(path: str) -> str:
info = read_elf_info(path)
if info[0] is None:
return "Unknown"
e_machine = info[2]
return arch_name(e_machine)
def is_arm_v7(path: str) -> bool:
info = read_elf_info(path)
return info[0] is not None and info[2] == EM_ARM
============================= Core logic =====================================
Result = Tuple[str, str, str, str, str] # (status_type, notes, symbol, alignment, filepath, arch) - aligns w/ Bash script idea
def check_so_alignment(so_file: str, relative_path: str) -> Result:
if not os.path.isfile(so_file):
return ("ERROR", "File not found", "❌", "0B", relative_path, "Unknown")
# Detect ELF
with open(so_file, "rb") as f:
magic = f.read(4)
if magic != ELF_MAGIC:
return ("ERROR", "Not an ELF file", "❌", "Unknown", relative_path, "Unknown")
arch = get_arch(so_file)
if is_arm_v7(so_file):
return ("PASS", "ARM v7 - 16KB not required", "✅", "N/A", relative_path, arch)
max_exp = max_load_align_exponent(so_file)
if max_exp is None:
return ("ERROR", "Unknown alignment", "❌", "Unknown", relative_path, arch)
# Human display for alignment
if max_exp >= 10:
kb = 1 << (max_exp - 10)
alignment_disp = f"{kb}KB"
else:
b = 1 << max_exp
alignment_disp = f"{b}B"
if max_exp >= 14:
return ("PASS", ">=16KB aligned", "✅", alignment_disp, relative_path, arch)
else:
return ("FAIL", "Need 16KB alignment", "❌", alignment_disp, relative_path, arch)
def process_results(results: List[Result]):
total_so = 0
aligned_so = 0
failed_so = 0
passes: List[Tuple[str,str,str,str,str]] = []
fails: List[Tuple[str,str,str,str,str]] = []
for r in results:
if not r:
continue
total_so += 1
status_type, notes, symbol, alignment, filepath, arch = r
if status_type == "PASS":
aligned_so += 1
passes.append((symbol, filepath, arch, alignment, notes))
else:
failed_so += 1
fails.append((symbol, filepath, arch, alignment, notes))
if passes:
print(f"\n{GREEN}✅ Compatible Libraries{NC}")
print_table_header()
for symbol, filepath, arch, alignment, notes in passes:
print_table_row(symbol, filepath, arch, alignment, notes)
if fails:
print(f"\n{RED}❌ Not Compatible Libraries{NC}")
print_table_header()
for symbol, filepath, arch, alignment, notes in fails:
print_table_row(symbol, filepath, arch, alignment, notes)
print("")
print(hrule())
print(f"{BLUE}📊 SUMMARY{NC}")
print(f"Total .so files: {total_so}")
print(f"16KB Aligned (>=): {GREEN}{aligned_so}{NC}")
print(f"Not aligned: {RED}{failed_so}{NC}")
if failed_so == 0:
print(f"\n{GREEN}🎉 All .so files are properly aligned!{NC}")
else:
print(f"\n{RED}⚠️ Some .so files need alignment fixes{NC}")
def process_apk(apk_file: str):
print(f"{BLUE}📱 Processing APK: {apk_file}{NC}")
print("=================================================")
results: List[Result] = []
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as temp_dir:
try:
with zipfile.ZipFile(apk_file, 'r') as z:
z.extractall(temp_dir)
except Exception as e:
print(f"{RED}❌ Failed to extract APK file: {e}{NC}")
return
for root, _, files in os.walk(temp_dir):
for name in files:
if name.lower().endswith(".so"):
so_path = os.path.join(root, name)
rel_path = os.path.relpath(so_path, temp_dir)
results.append(check_so_alignment(so_path, rel_path))
if not results:
print(f"{YELLOW}⚠️ No .so files found in APK{NC}")
return
process_results(results)
def process_single_so(so_file: str):
print(f"{BLUE}🔍 Processing single .so file: {so_file}{NC}")
print("=================================================")
result = check_so_alignment(so_file, os.path.basename(so_file))
process_results([result])
def process_directory(directory: str):
print(f"{BLUE}📁 Processing directory: {directory}{NC}")
print("=================================================")
results: List[Result] = []
for root, _, files in os.walk(directory):
for name in files:
if name.lower().endswith(".so"):
so_path = os.path.join(root, name)
rel_path = os.path.relpath(so_path, directory)
results.append(check_so_alignment(so_path, rel_path))
if not results:
print(f"{YELLOW}⚠️ No .so files found in directory{NC}")
return
process_results(results)
def main():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Check .so PT_LOAD alignment (>=16KB) inside ELF files, dirs, or APKs.")
parser.add_argument("input", help="Path to .apk, .so, or a directory")
args = parser.parse_args()
inp = args.input
if not os.path.exists(inp):
print(f"{RED}❌ Invalid input: not found{NC}")
sys.exit(1)
if os.path.isfile(inp):
lower = inp.lower()
if lower.endswith(".apk"):
process_apk(inp)
elif lower.endswith(".so"):
process_single_so(inp)
else:
print(f"{RED}❌ Unsupported file type (expected .apk or .so){NC}")
sys.exit(1)
elif os.path.isdir(inp):
process_directory(inp)
else:
print(f"{RED}❌ Invalid input{NC}")
sys.exit(1)
if name == “main”:
main()
(4) 运行命令:
python check_page_alignment_python.py xxx.apk
(5) 运行结果:
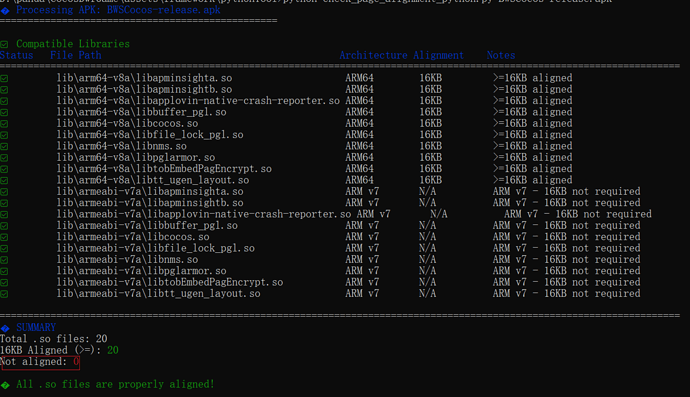
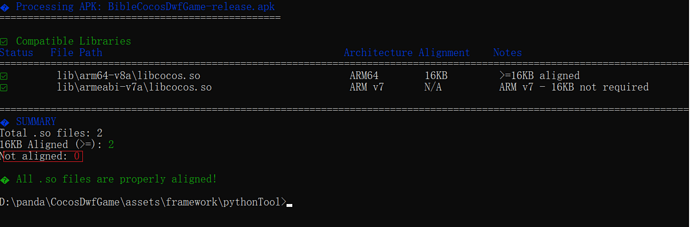
从截图看,arm64-v8a 的 .so 都“>=16KB aligned”,是符合 16KB 页对齐要求的;“ARM v7 – 16KB not required” 表示这些 32 位 armeabi-v7a 库不受 16KB 对齐强制要求的约束,属于豁免项,显示 N/A 属于预期。
7、使用 zipalign 检测
zipalign 是 Android SDK Build-Tools 自带的命令行工具,用来给 APK 做 ZIP 条目对齐。其作用是让 APK 中未压缩的资源(尤其是 .so)在设备上按页面边界直接映射读取,减少内存拷贝。为支持 16KB 页面大小,需使用带 -P 选项的新版本 zipalign(build-tools 35+)对齐/校验未压缩的 .so 为 16KB ZIP 对齐。参考官方文档:支持 16 KB 页面大小 · 更新打包方式。https://developer.android.com/guide/practices/page-sizes?hl=zh-cn#update-packaging
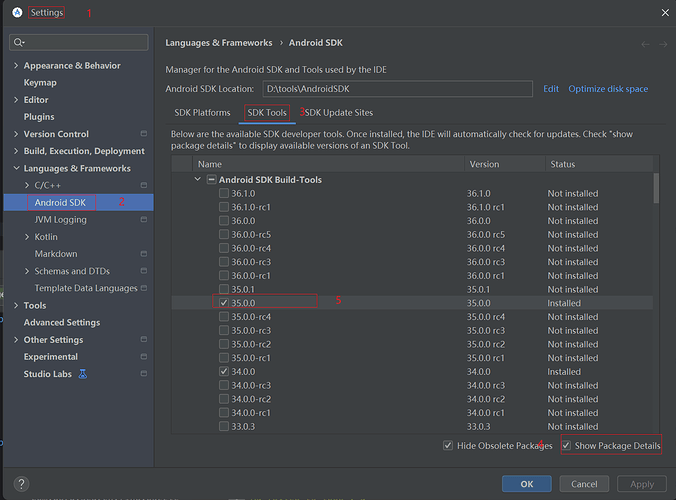
(1) 用 Android Studio 图形界面:安装 “Android SDK Build-Tools 35.0.0”(或更高)
-
安装后 zipalign 位于:
-
C:\Users<你的用户名>\AppData\Local\Android\Sdk\build-tools\35.0.0\zipalign.exe
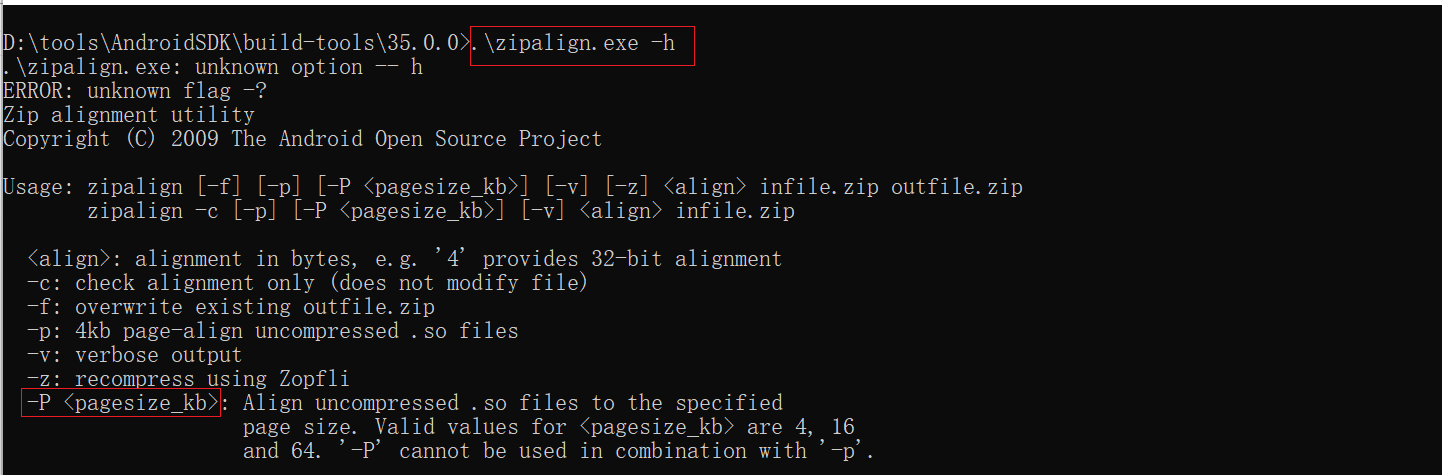
1) 先确认 zipalign 版本支持 -P
.\zipalign.exe -h
应看到 “-P <pagesize_kb>”
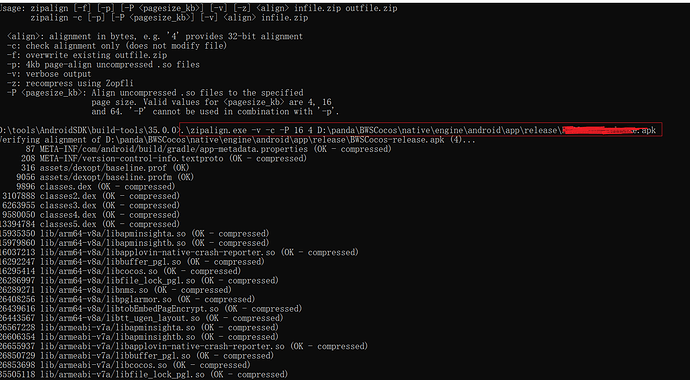
2)校验 APK 是否为 16KB ZIP 对齐(把路径换成你的 APK;路径有空格要用引号)
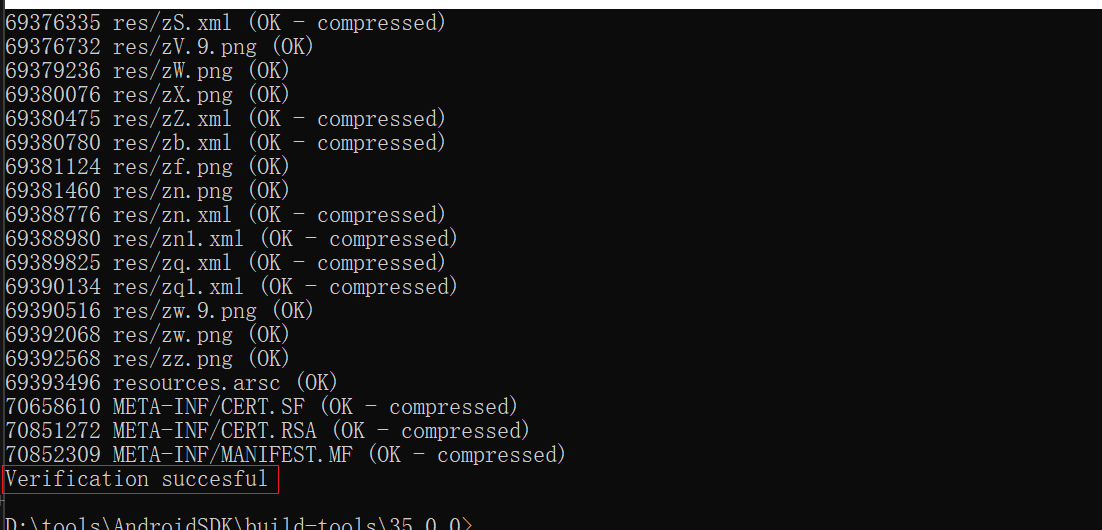
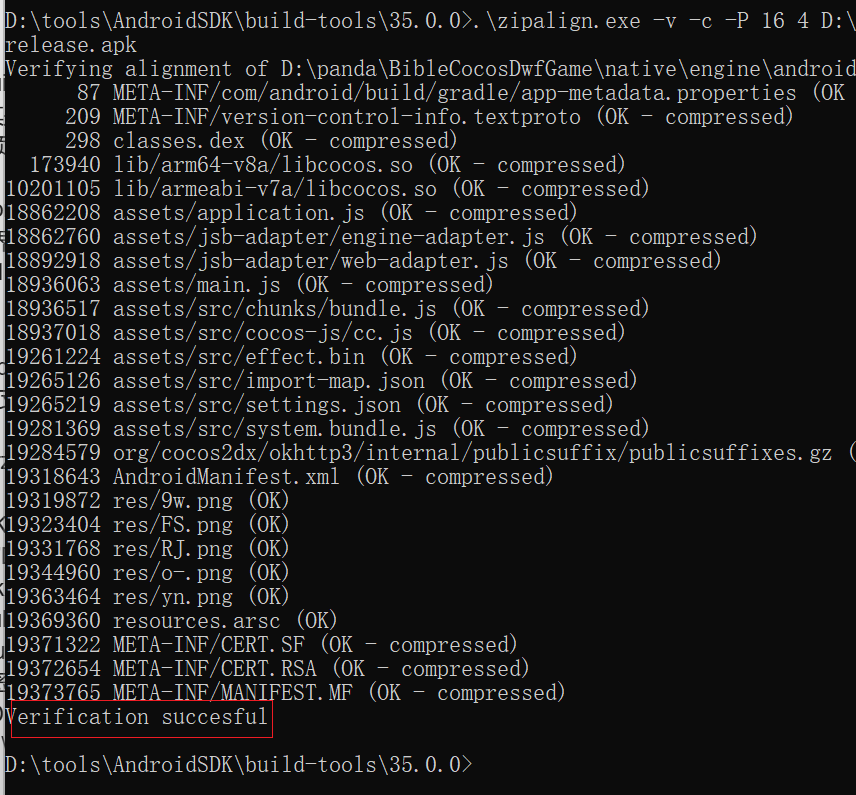
.\zipalign.exe -v -c -P 16 4 “D:\你的路径\xxx.apk”
出现 “Verification successful” 即通过。
3)若未通过:先对齐未签名包,再签名
.\zipalign.exe -f -p 16384 “D:\path\app-release-unsigned.apk” “D:\path\app-release-zipaligned.apk”
.\apksigner.bat sign --ks “D:\path\your.jks” --ks-key-alias yourAlias “D:\path\app-release-zipaligned.apk”
8、3.8.5 版本适配 16KB
(1) 开始步骤和 3.8.3 一致,3.8.5 引擎需要修改两个文件
1)AndroidPlatform.cpp
856行左右:将 ALooper_pollAll 改为 ALooper_pollOnce
2)jsb_global_init.cpp
52行左右:
将 static std::basic_string xxteaKey; 改为 static std::vector xxteaKey;
(2) 16 KB 进行检测
1)zipalign 检测(直接将 apk 拖进来即可)
.\zipalign.exe -v -c -P 16 4 D:\你的路径\xxx.apk
2) python 脚本检测
python check_page_alignment_python.py xxx.apk