可以,你的帖子我都不用在收藏找,太好搜了。(吐槽下,收藏的功能要用的时候基本找不到  )
)
跟营销号学的,还可以吧? 
可以可以,我这个是入门版,你是进阶版
必须的,相当于品牌商标
学到了,学到了。以后资源加载这块就很nice 了
继续对应下具体业务中会遇到什么问题吗? 感觉遇到就是个坑.
最近正在用Promise做一个加载模块图集中素材的接口,做了作业练习了一下。
/**
* 异步加载指定路径的资源并执行回调函数
* @template LoadType 资源类型构造函数,必须继承自 cc.Asset
* @template CallbackResult 回调函数的返回类型
* @param {string} path 资源路径,格式为"bundle名称/资源路径"
* @param {LoadType} type 要加载的资源类型(构造函数)
* @param {(asset: InstanceType<LoadType>) => CallbackResult} callback 加载完成后执行的回调函数(参数为资源实例)
* @returns {Promise<CallbackResult>} 返回包含回调结果的Promise
* @throws {Error} 当加载bundle或资源失败时抛出错误
* @deprecated 未对资源进行引用计数管理
* @example
* loadAsset2('resources/Texture/Images/imageName', cc.SpriteFrame, (loadAssert): void => {
this.testLoadSprite.spriteFrame = loadAssert
})
*/
async function loadAsset2<LoadType extends typeof Asset, CallbackResult>(
path: string,
type: LoadType,
callback: (asset: InstanceType<LoadType>) => CallbackResult
): Promise<CallbackResult> {
const slashIndex: number = path.indexOf('/');
const bundleName: string = path.slice(0, slashIndex);
const assetPath: string = path.slice(slashIndex + 1);
// 加载bundle
const bundle: AssetManager.Bundle = await new Promise<AssetManager.Bundle>((resolve, reject) => {
assetManager.loadBundle(bundleName, (err: Error, bundle: AssetManager.Bundle): void => {
if (err) reject(err);
else resolve(bundle);
});
});
// 加载资源
const asset: InstanceType<LoadType> = await new Promise<InstanceType<LoadType>>((resolve, reject) => {
bundle.load(assetPath, type, (err: Error, loadedAsset: InstanceType<LoadType>): void => {
if (err) reject(err);
else resolve(loadedAsset);
});
});
// 执行回调
return callback(asset);
}
优点:做了泛型,类型更安全
缺点:这个方法取的是资源因此不需要resolve(bundle),异步方法无需callback直接resolve(asset)
如果是要显示加载进度还是需要回调的
加载单个资源进度获取不到吧,加载bundle可以取到的
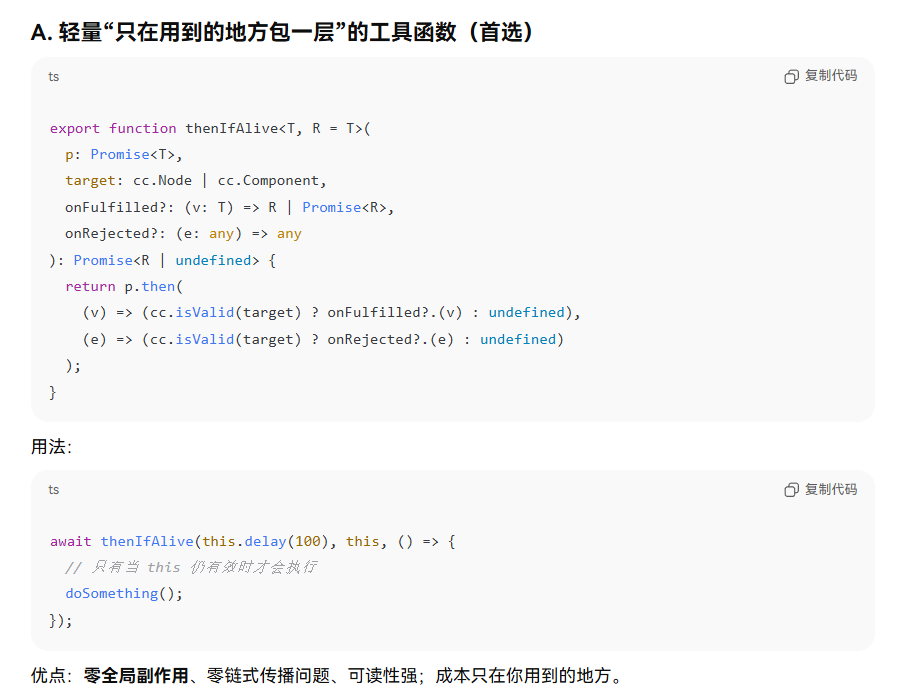
其实使用await也要小心,当你的view被干掉了,但是你的delay还没有被清掉,时间到了会继续执行后面的代码,这个this已经无效了
const weakMap = new WeakMap(); // 全局弱引用映射
if (CC_DEV) {
window["my_weakMap "] = weakMap
}
const thenFunc = Promise.prototype.then
Promise.prototype.then = function (onFulfilled, onRejected) {
const that = this
return thenFunc.call(this,
function (value) {
if (typeof onFulfilled === 'function') {
const targetRef = weakMap .get(that);
if (targetRef && !cc.isValid(targetRef)) {
console.warn('Promise liftTarget Component is invalid, skip then callback')
// onRejected?.("liftTarget this is valid")
return;
}
return onFulfilled(value)
}
return value;
},
onRejected)
}
Promise.prototype.isValid= function (target: cc.Node | cc.Component) {
if (!target) return this;
weakMap .set(this, target); // 键是 Promise 实例,值是被弱引用的 target
return this;
}
declare global {
/**全局hook */
interface Promise<T> {
/**处理异步后生命周期问题 */
isValid: (target: cc.Component | cc.Node) => Promise<any>
}
}
//使用示例
await this.delay(100).isVaild(this) //当this 无效后 不会执行后面代码了
后来为了弄这个,我新增了isVaild方法,AI说尽量不这样扩展,但是这是改动已有代码的无二选择了,不然得在所有的await地方去判断 this是不是null,是不是还有效
该代码已经上线运行了,目前没什么问题
嗯,异步是会有这个问题
当初这样写了,AI这样说过 改动太多了 莫法  受限当前业务中 只有一层的then,所以还好 可以在失效的时候 return value出去, 业务底层都是使用的resolve(null) 来处理错误 所以不存在reject的问题,可以根据自己的情况改动
受限当前业务中 只有一层的then,所以还好 可以在失效的时候 return value出去, 业务底层都是使用的resolve(null) 来处理错误 所以不存在reject的问题,可以根据自己的情况改动
还是因为js的promise没有中断,不然全局处理下就行了~
是的,它本身没有提供 ,不管使用第三方或者使用代理的形式,都会在其他使用的地方大量穿插
做非法判断就行
还可以补充几个 比如操作必须按照顺序执行的时候用就特别方便
async processOrder(orderId) {
await validateOrder(orderId);
await processPayment(orderId);
await updateInventory(orderId);
await sendConfirmation(orderId);
}
这种就不好 会顺序执行影响效率
async fetchAllData() {
const users = await fetchUsers();
const products = await fetchProducts();
return { users, products };
}
换成这样并行执行就行了
async fetchAllData() {
const [users, products] = await Promise.all([
fetchUsers(),
fetchProducts()
]);
return { users, products };
}
但是比如单词的时候其实没必要使用比如
async simpleFetch() {
const response = await fetch(’/api/data’);
return response.json();
}
这个写法其实不如
simpleFetch() {
return fetch(’/api/data’).then(response => response.json());
}
还有一个 我经常用的小技巧 解决await reject的问题
public static awaitTo(promise: Promise) {
if (promise) {
return promise
.then(data => [null, data])
.catch(err => [err, null]);
}
else {
Promise.resolve()
}
}
封装一个后用起来贼简洁
这是两回事,虽然在这个问题下,可能想解决的是一回事