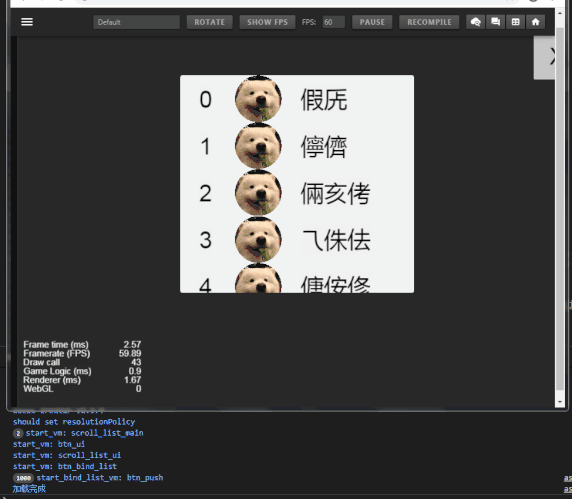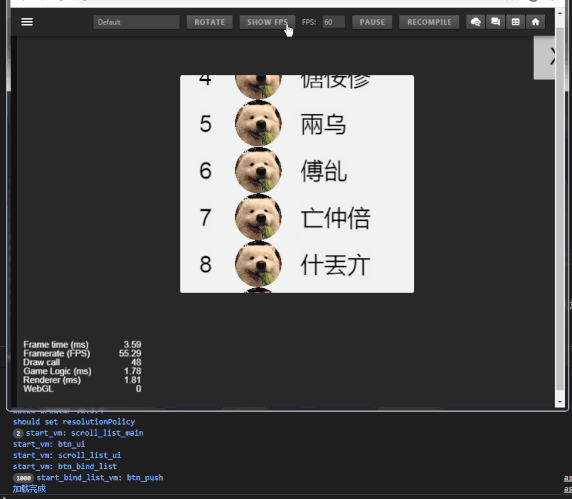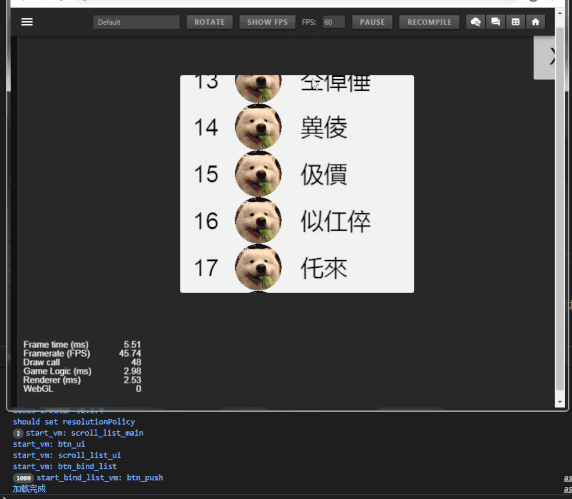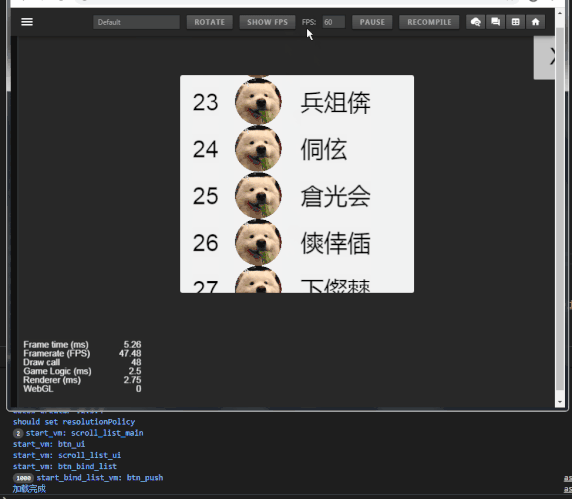
话不多说,上效果:
示例数据
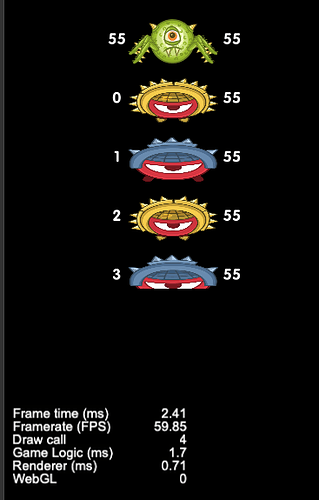
- 列表item数:1000
- draw call:43~48
可以看到 draw call 一直在45左右徘徊,(FPS低是因为录屏)。
下面上代码
const {ccclass, property, menu} = cc._decorator;
/**列表draw call优化组件 */
@ccclass
@menu("tool/list_optimize")
export default class list_optimize extends cc.Component {
/* --------------------------------segmentation-------------------------------- */
onLoad() {
if (!this.node.scroll_view) {
cc.error("不存在ScrollView组件!");
return;
}
// ------------------事件监听
this.node.on("scrolling", this._event_update_opacity, this);
this.node.scroll_view.content.on(cc.Node.EventType.CHILD_REMOVED, this._event_update_opacity, this);
this.node.scroll_view.content.on(cc.Node.EventType.CHILD_REORDER, this._event_update_opacity, this);
}
/* ***************功能函数*************** */
/**获取在世界坐标系下的节点包围盒(不包含自身激活的子节点范围) */
private _get_bounding_box_to_world(node_o_: any): cc.Rect {
let w_n: number = node_o_._contentSize.width;
let h_n: number = node_o_._contentSize.height;
let rect_o = cc.rect(
-node_o_._anchorPoint.x * w_n,
-node_o_._anchorPoint.y * h_n,
w_n,
h_n
);
node_o_._calculWorldMatrix();
rect_o.transformMat4(rect_o, node_o_._worldMatrix);
return rect_o;
}
/**检测碰撞 */
private _check_collision(node_o_: cc.Node): boolean {
let rect1_o = this._get_bounding_box_to_world(this.node.scroll_view.content.parent);
let rect2_o = this._get_bounding_box_to_world(node_o_);
// ------------------保险范围
rect1_o.width += rect1_o.width * 0.5;
rect1_o.height += rect1_o.height * 0.5;
rect1_o.x -= rect1_o.width * 0.25;
rect1_o.y -= rect1_o.height * 0.25;
return rect1_o.intersects(rect2_o);
}
/* ***************自定义事件*************** */
private _event_update_opacity(): void {
this.node.scroll_view.content.children.forEach(v1_o=> {
v1_o.opacity = this._check_collision(v1_o) ? 255 : 0;
});
}
}
原理:通过检测 item 与列表可视区域的碰撞,如果碰撞到了那么即判断为在可视区域内,将 item 的 opacity 设为255,反之为0.
注:
-
本代码使用了nodes扩展,例如
this.node.scroll_view可以替换为 this.node.getComponent(cc.ScrollView),如对nodes感兴趣的朋友请看
[muzzik分享]: NodeS扩展,优雅的获取节点和组件方式 -
我该怎么使用它?:将上方代码复制到新建脚本内挂载到ScrollView所在节点即可,若你未使用nodes需将部分代码替换,如:this.node.scroll_view 替换为 this.node.getComponent(cc.ScrollView)
-
此组件将为你做什么?:在不影响其他数据 or 组件的同时为你优化列表的draw call,网格、横、纵列表全搞定,另外此组件还可优化非固定大小item的draw call。
代码块讲解:
this.node.on("scrolling", this._event_update_opacity, this);
this.node.scroll_view.content.on(cc.Node.EventType.CHILD_REMOVED, this._event_update_opacity, this);
this.node.scroll_view.content.on(cc.Node.EventType.CHILD_REORDER, this._event_update_opacity, this);
这里监听了列表的滑动、子节点移除、子节点层级改变,一旦触发就更新展示
/**获取在世界坐标系下的节点包围盒(不包含自身激活的子节点范围) */
private _get_bounding_box_to_world(node_o_: any): cc.Rect {
let w_n: number = node_o_._contentSize.width;
let h_n: number = node_o_._contentSize.height;
let rect_o = cc.rect(
-node_o_._anchorPoint.x * w_n,
-node_o_._anchorPoint.y * h_n,
w_n,
h_n
);
node_o_._calculWorldMatrix();
rect_o.transformMat4(rect_o, node_o_._worldMatrix);
return rect_o;
}
_get_bounding_box_to_world 函数的作用和注释一样,其实 cc.Node 本来就有个getBoundingBoxToWorld函数,那我为什么没有使用它呢?因为它返回的矩形范围包括了已激活的子节点大小,就是说矩形范围可能会超出当前节点的真实大小,所以我截取了这函数代码的一部分用来单独使用。
/**检测碰撞 */
private _check_collision(node_o_: cc.Node): boolean {
let rect1_o = this._get_bounding_box_to_world(this.node.scroll_view.content.parent);
let rect2_o = this._get_bounding_box_to_world(node_o_);
// ------------------保险范围
rect1_o.width += rect1_o.width * 0.5;
rect1_o.height += rect1_o.height * 0.5;
rect1_o.x -= rect1_o.width * 0.25;
rect1_o.y -= rect1_o.height * 0.25;
return rect1_o.intersects(rect2_o);
}
_check_collision函数中上半部分很好理解,对于其中的保险范围可以理解为为了防止列表滑动过快时节点激活展示的速度跟不上,所以需要提前激活,而提前激活的办法就是扩大列表矩形的范围,这里我把宽、高分别扩大了各自的1/2,至于调整x,y是为了让其上下左右对齐,因为矩形的x,y是指其左下角,也就是左下角才是锚点,所以需要调整坐标。

 ,商业项目谁不优化?
,商业项目谁不优化?